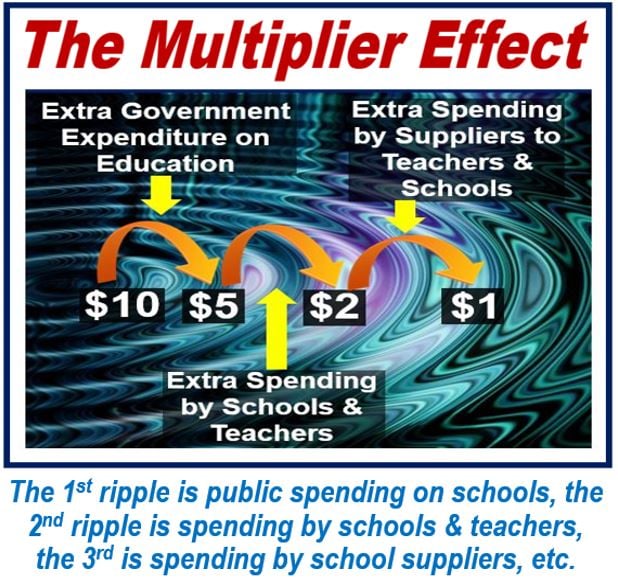
What is the multiplier effect? Definition and examples Market Business News
Rumus Multiplier Effect. Terdapat 2 jenis rumus multiplier effect, yaitu: k = 1 / MPS. atau . k = 1 / (1 - MPC) Dalam hal ini, rumus MPC atau (Marginal Propensity to Consume) dan MPS (Marginal Propensity to Save) dapat temukan dengan menggunakan rumus-rumus di bawah ini.

What is the multiplier effect? Definition and examples Market Business News
The multiplier effect doesn't just apply to government spending. For instance, if businesses invest in more equipment, or people buy more houses (both of which fall under the "private investment" bucket of GDP), that also triggers a chain reaction. Same with a change in consumer spending. An increase in our spending can ripple throughout.

3 Rumus Multiplier Effect pada Investasi
The money multiplier formula is simply 1/ r where r is the reserve ratio. This means that the smaller r is, the bigger the money multiplier is. Alternately, as r gets bigger, the money multiplier.

Multiplier Effect Penjelasan dan Contohnya Jurnal.id
KOMPAS.com - Multiplier effect merupakan konsep penting dalam ekonomi yang menjelaskan bagaimana perubahan dalam pengeluaran suatu sektor dapat memiliki efek berganda atau multiplikatif pada pendapatan nasional.. Apa itu multiplier effect?. Pengertian multiplier effect. Multiplier effect adalah keadaan di mana perubahan dalam pengeluaran suatu sektor ekonomi akan menghasilkan perubahan yang.

PPT Multiplier PowerPoint Presentation, free download ID5579107
In economics, the multiplier effect happens when the change in a particular economic input (e.g. government spending) causes a larger change in an economic output (e.g. gross domestic product). The multiplier effect was first theorized by economist Paul Samuelson in his paper " The Relation of Home Investment to Unemployment " (1931).

Apa itu Multiplier Effect dan Mengapa itu Penting? Kledo Blog
Rumus Angka Pengganda. Secara matematis, multiplier dapat dirumuskan dengan rumus angka pengganda. Foto: Pexels.com. Angka pengganda atau multiplier bisa dihitung secara matematis. Menurut Husna Ni'matul Uly dalam Ekonomi Makro Islam, rumus yang digunakan dalam perhitungan multiplier adalah sebagai berikut: k = 1/1-MPC atau k = 1/MPS.

Explaining the Multiplier Effect tutor2u Economics
The fiscal multiplier measures the impact of a fiscal stimulus on the Gross Domestic Product (GDP) of an economy. Fiscal stimulus is the increase in government spending to stimulate the economy. The fiscal multiplier should not be confused with the monetary multiplier, which is the impact of change in money supply on the output of an economy.

The Multiplier Effect (BEST AND EASIEST EXPLANATION) A Level Economics (2024) YouTube
Multiplier Effect: The multiplier effect is the expansion of a country's money supply that results from banks being able to lend. The size of the multiplier effect depends on the percentage of.

Explaining the Multiplier Effect tutor2u Economics
The Multiplier Effect. The Multiplier Effect is defined as the change in income to the permanent change in the flow of expenditure that caused it. In other words, the multiplier effect refers to the increase in final income arising from any new injections. Injections are additions to the economy through government spending, money from exports.
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/TermDefinitions_Multipliereffect_final-9e854bc90a204f839018cae80f82eec0.png)
What Is the Multiplier Effect? Formula and Example
Rumus Untuk Menentukan Multiplier Effect. Setelah mengetahui apa yang dimaksud dengan efek pengganda dan berbagai jenisnya, Anda harus mengetahui rumus untuk menghitungnya. Agar bisa menghitung multiplier effect, terdapat rumus yang bisa Anda gunakan. Rumus tersebut bisa Anda sesuaikan dengan jenis perhitungan yang akan Anda lakukan.

Multiplier Effect Adalah Pengertian, Fungsi, Rumus dan Jenis
The multiplier effect. 2 November 2019 by Tejvan Pettinger. The fiscal multiplier effect occurs when an initial injection into the economy causes a bigger final increase in national income. For example, if the government increased spending by £1 billion but this caused real GDP to increase by a total of £1.7 billion, then the multiplier would.

Explaining the Multiplier Effect tutor2u Economics
Once you have m, plug it into the formula ΔMS = m × ΔMB. So if m1 = 2.6316 and the monetary base increases by $100,000, the money supply will increase by $263,160. If m1 = 4.5 and MB decreases by $1 million, the money supply will decrease by $4.5 million, and so forth. Practice this in Exercise 2.+. 3.

PPT Pokok Bahasan 4 KESEIMBANGAN PENDAPATAN NASIONAL 3 SEKTOR PowerPoint Presentation ID4609404
Summary. Chapter 6 examines a number of key summary analytical measures known as multipliers that can be derived from input-output models to estimate the effects of exogenous changes on (1) new outputs of economic sectors, (2) income earned by households resulting from new outputs, and (3) employment generated from new outputs, (4) value.

RUMUS MENCARI ANGKA ATAU KOEFISIEN PENGGANDA (MULTIPLIER), MPC, DAN MPS YouTube
Di dalam rumus multiplier effect dikenal dua istilah yakni MPS dan MPC. MPS adalah maraginal propensity to save sementara MPC yakni marginal propensity to consume. Baik MPC dan MPS memiliki teknis perhitungan dan fungsi yang berbeda. MPC merupakan perbandingan antara peningkatan konsumsi dengan pertambahan pemasukan disposibel.

Rumus Multiplier Effect atau Angka Pengganda dalam Ekonomi Materi Ekonomi Kelas 10
Y = {1÷ (1—MPC)}xA. The term inside the brackets is the multiplier: 1÷ (1—MPC) Notice that since MPC is less than 1, then 1÷ (1—MPC) will be greater than 1. Also, the higher MPC, the higher the multiplier. If G is the component of A that changes, then the government spending multiplier GM is given by the multiplier we derived above (20.

3 Rumus Multiplier Effect pada Investasi
The multiplier effect arises because one agent's spending is another agent's income. When a spending project creates new jobs for example, this creates extra injections of income and demand into a country's circular flow. The negative multiplier effect occurs when an initial withdrawal or leakage of spending from the circular flow leads.