
Understanding Dystonia Down with Dystonia
Parkinson's disease (PD) is a neurogenerative disorder that affects movement. People with PD have symptoms like tremors, muscle rigidity, and slow movements. If you have PD, you may also.

Musician’s dystonia Practical Neurology
Unlike a seizure, dystonic movements do not rapidly recur within a few seconds or minutes. Dystonia is not associated with any change in consciousness or awareness. Symptoms of dystonia can include: Twisting of one side of the face, one arm, or one leg. A prolonged posture of the eyelids, face, arm, hand, leg, or foot.
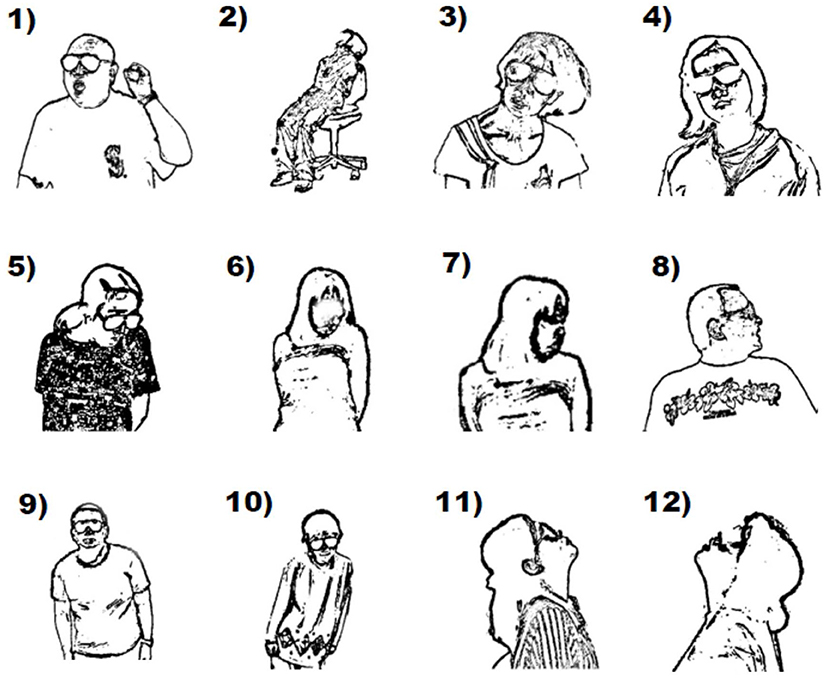

Frontiers Possible Commonalities of Clinical Manifestations Between Dystonia and Catatonia
Partington syndrome is a neurological disorder that causes intellectual disability along with a condition called focal dystonia that particularly affects movement of the hands. Partington syndrome usually occurs in males; when it occurs in females, the signs and symptoms are often less severe. The intellectual disability associated with.
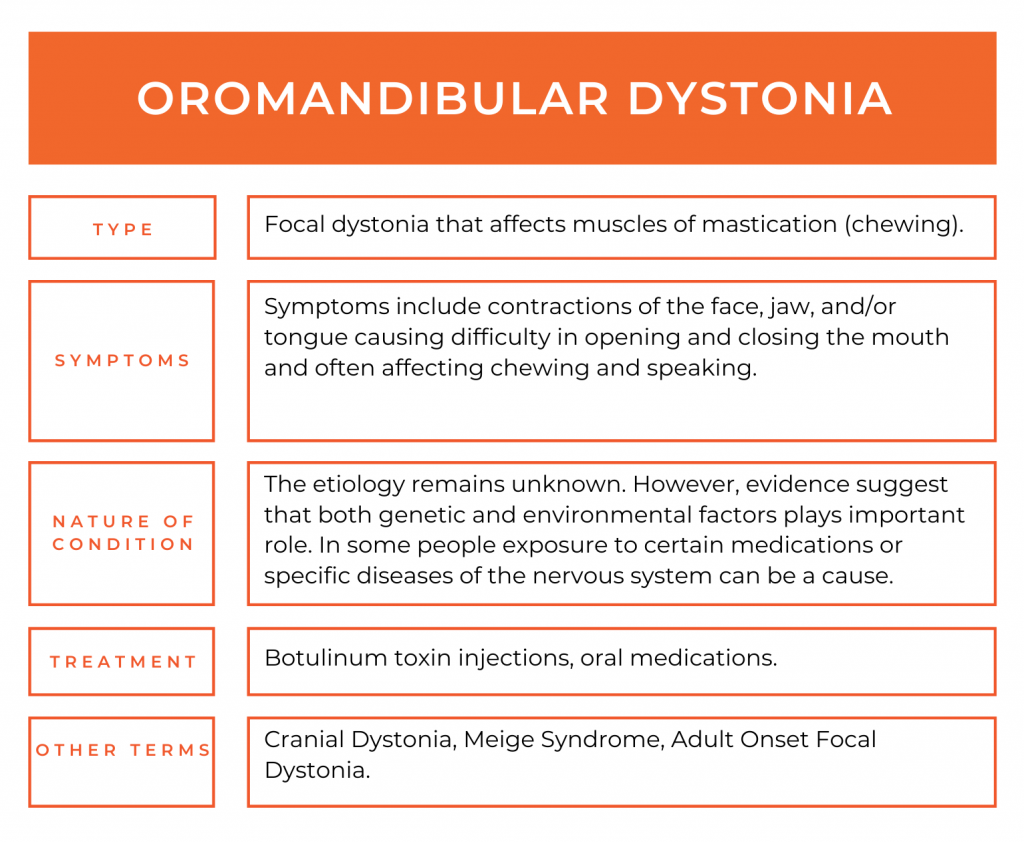
Oromandibular Dystonia Dystonia Europe
Dystonia is a dynamic disorder that changes in severity based on the activity and posture. Dystonia may assume a pattern of overextension or over-flexion of the hand, inversion of the foot, lateral flexion or retroflection of the head, torsion of the spine with arching and twisting of the back, forceful closure of the eyes, or a fixed grimace.
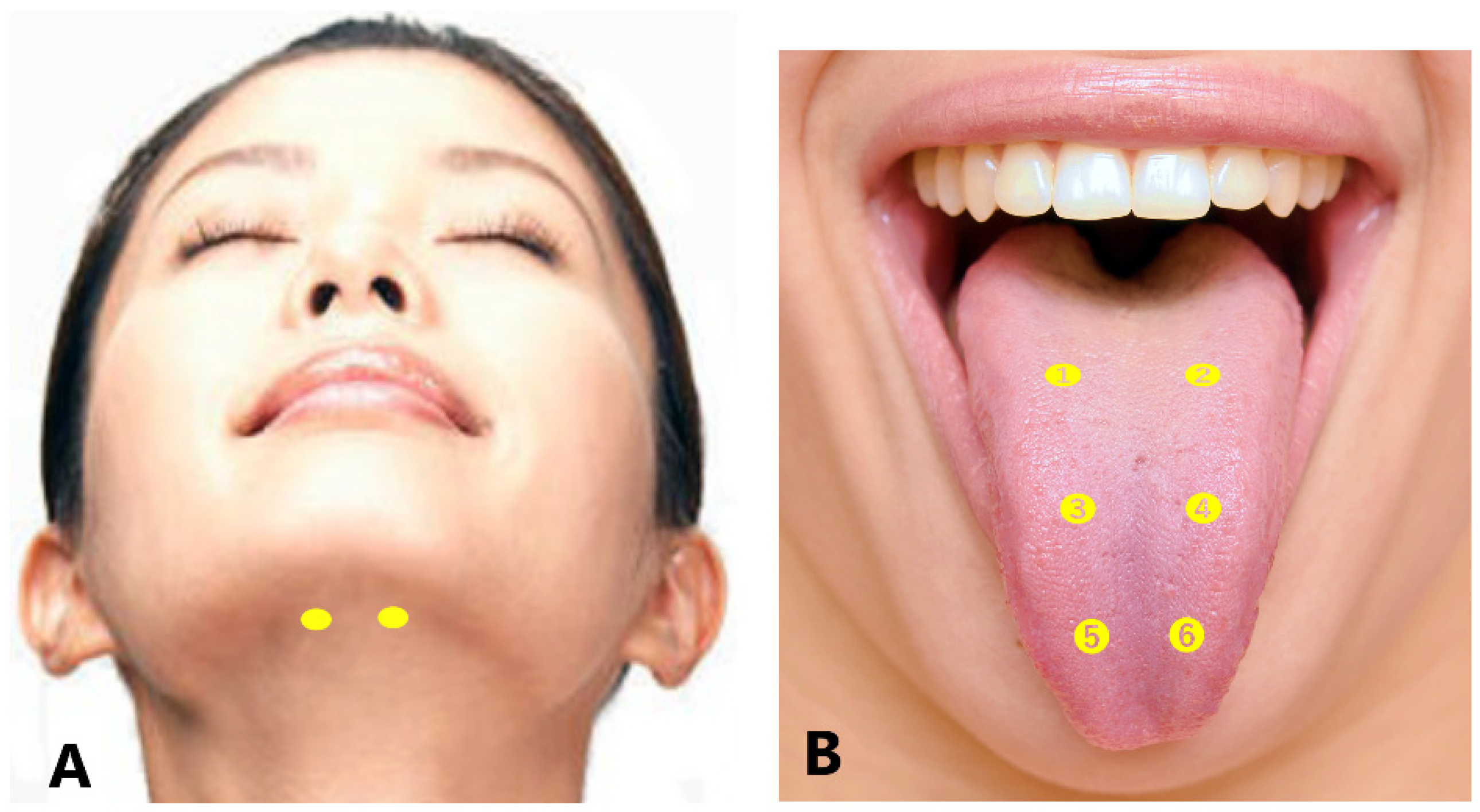
Botulinum Toxin Therapy for Oromandibular Dystonia Encyclopedia MDPI
The term "dystonic tremor" is used to describe tremor in those who have dystonia. Two mutually exclusive definitions of "dystonic tremor" were proposed. According to one definition, dystonic tremor is the tremor in the dystonic body part. An alternate definition of dystonic tremor entails irregular and jerky oscillations that have saw tooth.

Preview Dystonia Casebased Module YouTube
Dystonias. Dystonias are sustained involuntary muscle contractions of antagonistic muscle groups in the same body part, leading to sustained abnormal posturing or jerky, twisting, intermittent spasms that can resemble tremors, athetosis, or choreoathetosis. Dystonias can be primary or secondary and can be generalized, focal, or segmental.

Dystonia Sintomas at Sanhi Mediko.ph
Dystonia. Curled, clenched toes or a painful cramped foot are telltale signs of dystonia. Dystonia is a sustained or repetitive muscle twisting, spasm or cramp that can occur at different times of day and in different stages of Parkinson's disease (PD). Dystonia is a common early symptom of young-onset Parkinson's, but it can appear during.

3 Types of Dystonia in Parkinson Disease YouTube
Dystonia is a movement disorder characterized by sustained or intermittent muscle contractions causing abnormal, often repetitive movements, postures, or both; dystonic movements are typically patterned and twisting, and may be tremulous. Dystonia is often initiated or worsened by voluntary action and associated with overflow muscle activation.
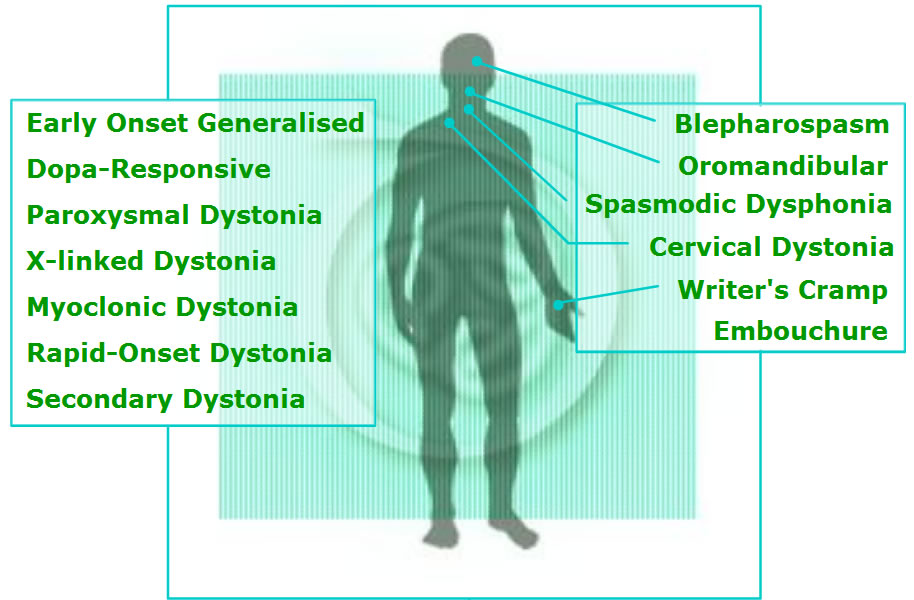
Forms of Dystonia Dystonia Ireland
Dystonia is a movement disorder in which some of your body's muscles contract in ways you can't control. This can cause your body to twist and move in awkward ways. Dystonia can affect one muscle.

Dystonia awareness information. Awareness, Understanding, Disorders
Dystonia. Brain, Nerves and Spine. Dystonia is a disorder that affects the way the body moves. It causes the muscles to contract, which makes them move involuntarily or get stuck in an abnormal position. Dystonia can affect the entire body or a certain part, and the movements can sometimes cause pain.

DystoniaCausesSignsSymptomsTreatmentTypesDiagnosis
Paroxysmal dystonia can cause tremor, pain, and twisting of the body, limbs, or face. It can resemble a seizure, but the person does not lose awareness or sensation. It can last from a few minutes.

[PDF] The pathophysiology of primary dystonia
Dystonia is a movement disorder that causes the muscles to contract involuntarily. This can cause repetitive or twisting movements. The condition can affect one part of your body (focal dystonia), two or more adjacent parts (segmental dystonia), or all parts of your body (general dystonia). The muscle spasms can range from mild to severe.

dystonia toes YouTube
Introduction. Dystonia is defined by "sustained or intermittent muscle contractions that lead to abnormal movements, postures, or both" (Fahn 1988).The most recent consensus definition of dystonia includes tremor and highlights that dystonic movements are "typically patterned, twisting, and may be tremulous, initiated or worsened by voluntary action and associated with overflow muscle.

Chiropractor treats a case of Dystonia Lyons Road
Dystonia is a nervous system disorder that causes uncontrollable muscle contractions, meaning a person's muscles tense up without trying to make the muscles do so. Though it affects muscles, it's actually an issue with your brain or another part of your nervous system. The name "dystonia" is a combination of the Latin prefix "dys.

Generalized Dystonia / Cervical dystonia, Dysphonia, Oromandibular dystonia / 전신 디스토니아 치료사례
Dystonia is a neurological movement disorder that results in unwanted muscle contractions or spasms. The involuntary twisting, repetitive motions, or abnormal postures associated with dystonia can affect anyone at any age. The movements can be slow or fast, range from mild to severe and happen predictably or randomly.

Pathogenesis of dystonia is it of cerebellar or basal ganglia origin? Journal of Neurology
Dystonia is a very complex, highly variable neurological movement disorder characterized by involuntary muscle contractions. As many as 250,000 people in the United States have dystonia, making it the third most common movement disorder behind essential tremor and Parkinson's disease.It is a condition that knows no age, ethnic or racial boundaries - it can affect young children to older.