
Human Nerve Cell Labeled Diagram From the Ground
Nerve Cell Labeling by Isabella Meader 522 plays 8 questions ~20 sec English 8p More too few (you: not rated) Tries 8 [?] Last Played February 22, 2022 - 12:00 am There is a printable worksheet available for download here so you can take the quiz with pen and paper. From the quiz author Help label the parts of the Nerve Cell! Remaining 0 Correct 0

What Is a Neuron? Diagrams, Types, Function, and More
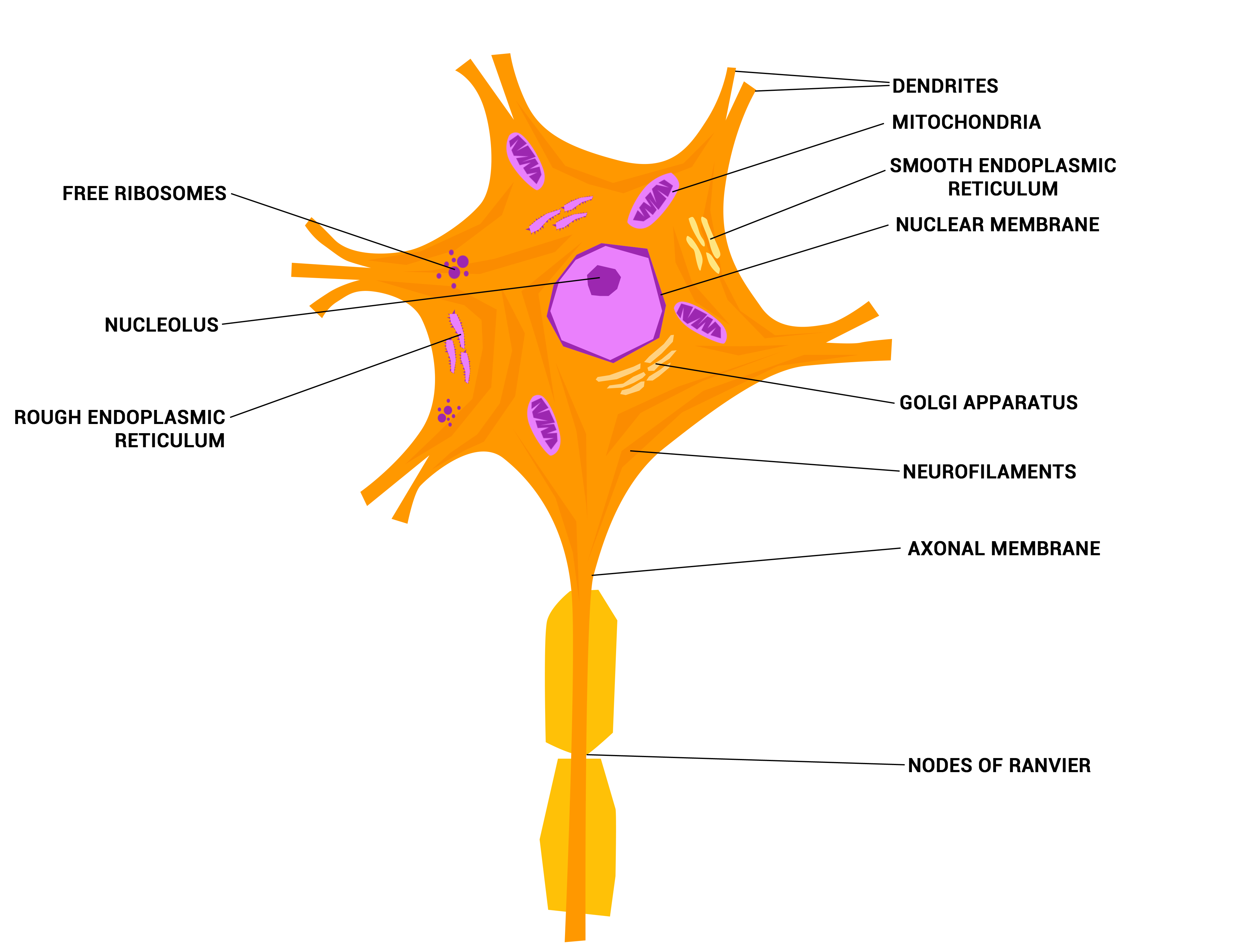
Parts of the Nerve Cell and Their Functions Silvia Helena Cardoso, PhD [1. Cell body] [2.Neuronal membrane][3.Dendrites] [4. Axon][5. Nerve ending] 1. Cell body The (soma) is the factory of the neuron. It produces all the proteins for the dendrites,axons and synaptic terminals and contains specialized organelles such asthe mitochondria, Golgi.
Neurons The crazy wires in our body. Doc Jana
Nervous System - Neuron: Nerve Cell Name: Choose the correct names for the parts of the neuron. (1) (2) (3) (4) (5) (6) This neuron part receives messages from other neurons. (7) This neuron part sends on messages to other neurons. (8) This neuron part gives messages to muscle tissue. (9) This neuron part processes incoming messages.
Nerve Tissue SEER Training
(A) Diagram of nerve cells and their component parts. (B) Axon initial segment (blue) entering a myelin sheath (gold). (C) Terminal boutons (blue) loaded with synaptic vesicles (arrowheads) forming synapses (arrows) with a dendrite (purple). (D) Transverse
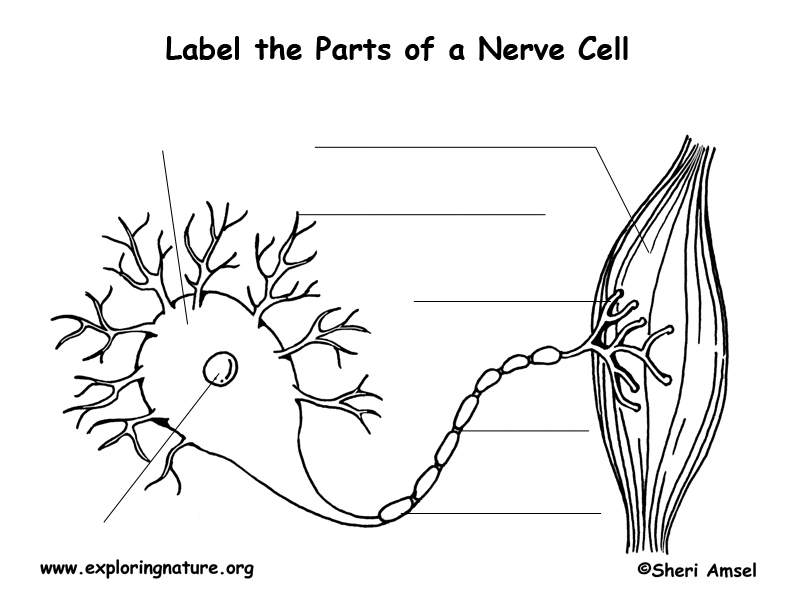
Nerve Cell (Neuron) Labeling Page
The neuron (or nerve cell) is the functional unit of both the central nervous system (CNS) and the peripheral nervous system (PNS). The basic functions of neurons can be summarized into three main tasks: receiving signals, integrating these signals and transmitting the signals to target cells and organs.
Nervous System The Partnership in Education
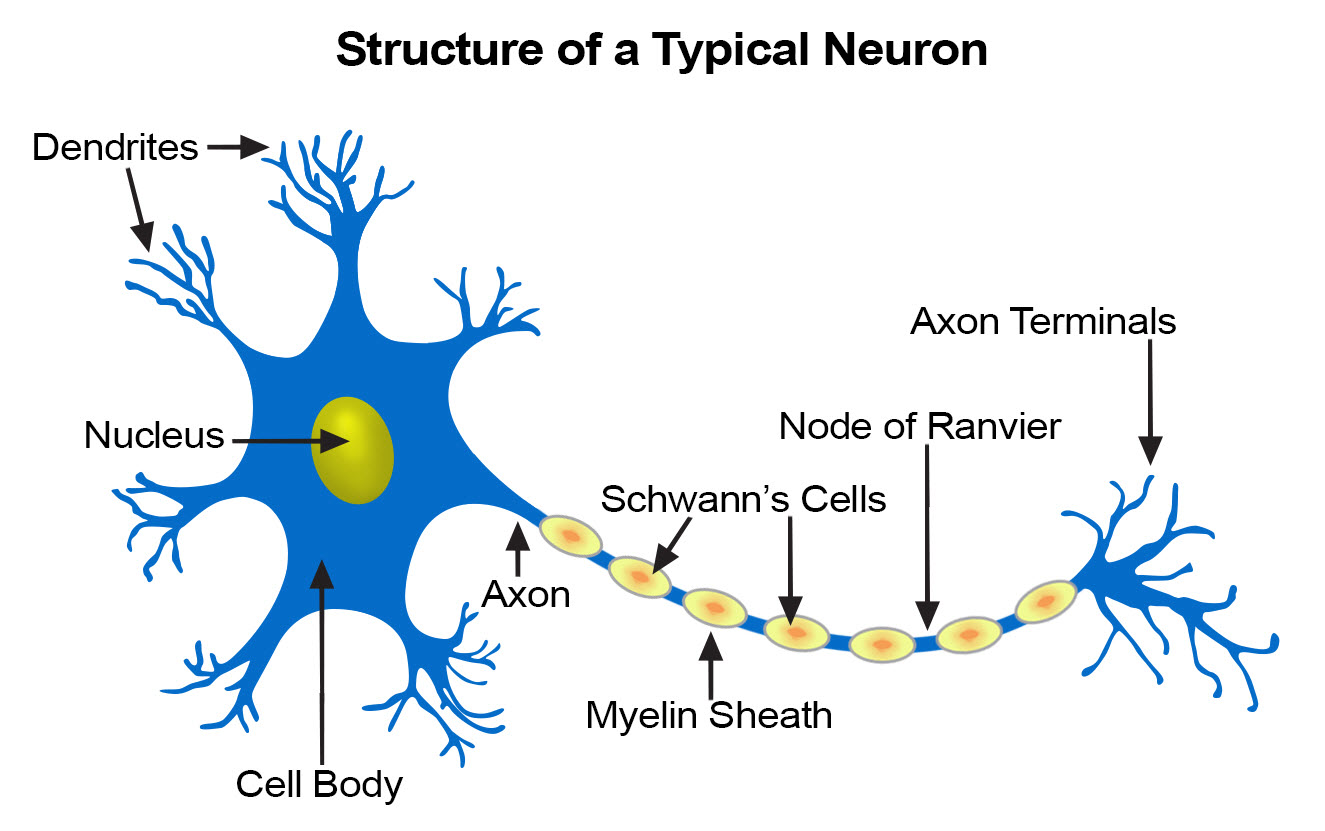
Parts of an Axon. a) Axon hillock - The part of the axon which remains attached to the cell body or soma. b) Myelin sheath - The layer of fatty acid produced from specialized cells called Schwann cells that are wrapped around the axon. c) Nodes of Ranvier - The gaps between the discontinuous myelin sheath that is running along the axon.
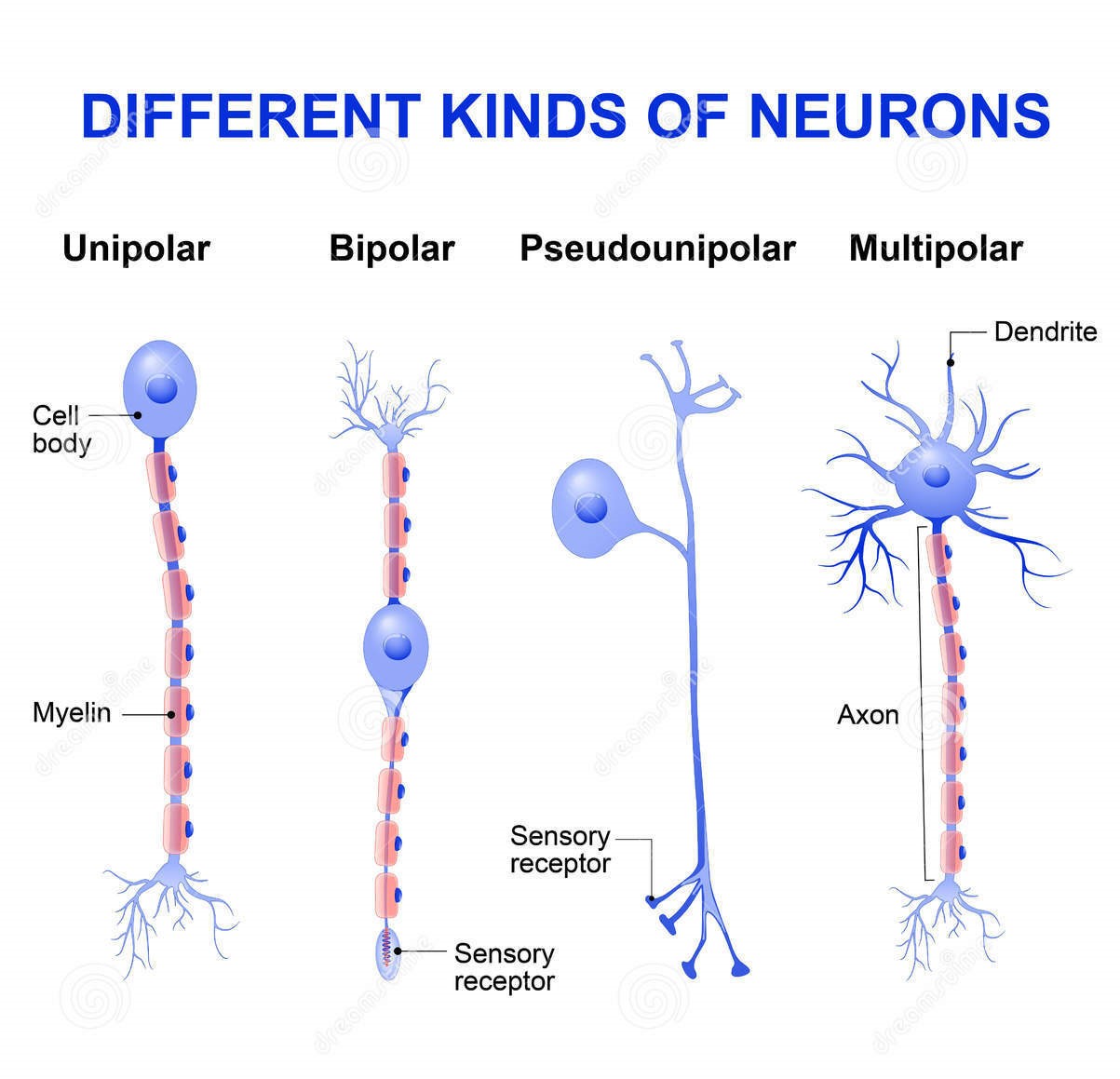
Structure and types of neuron (The nervous tissue) Online Science Notes
AboutTranscript. Neurons (or nerve cells) are specialized cells that transmit and receive electrical signals in the body. Neurons are composed of three main parts: dendrites, a cell body, and an axon. Signals are received through the dendrites, travel to the cell body, and continue down the axon until they reach the synapse (the communication.
.PNG)
Nervous system Presentation Health and Disease
Neuron. Within a nervous system, a neuron, neurone, or nerve cell is an electrically excitable cell that fires electric signals called action potentials across a neural network. Neurons communicate with other cells via synapses, which are specialized connections that commonly use minute amounts of chemical neurotransmitters to pass the electric.
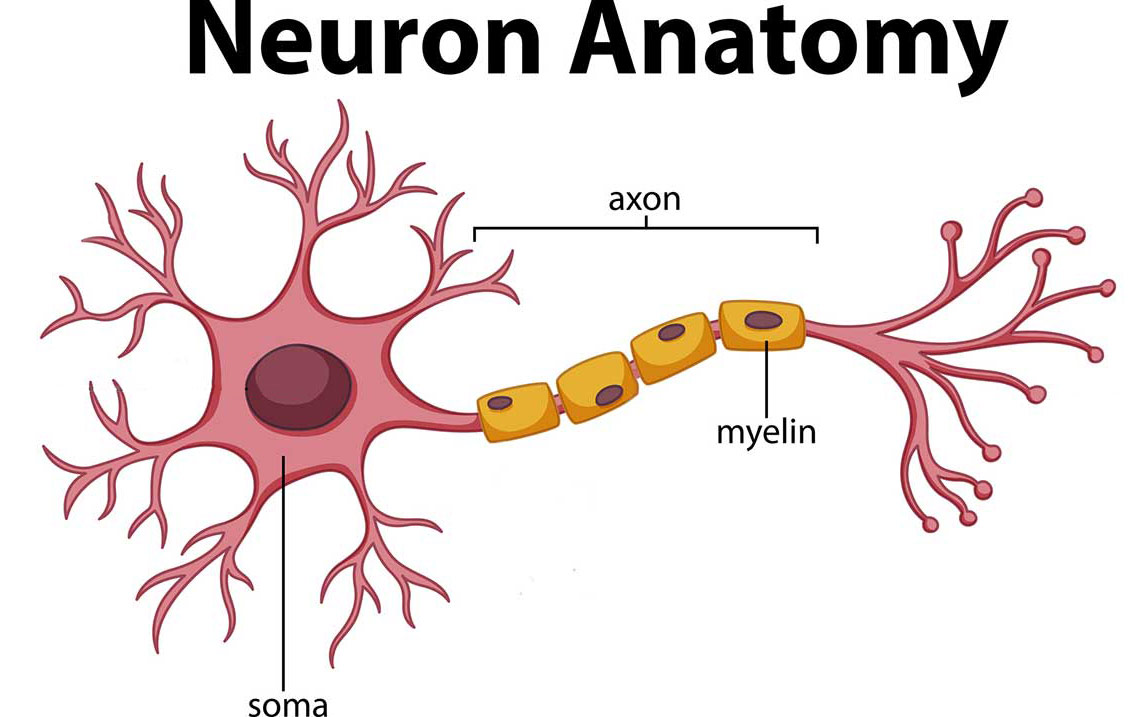
Brain Anatomy and How the Brain Works Johns Hopkins Medicine
The nervous system is a network of neurons whose main feature is to generate, modulate and transmit information between all the different parts of the human body. This property enables many important functions of the nervous system, such as regulation of vital body functions ( heartbeat, breathing, digestion), sensation and body movements.

12.2 Nervous Tissue Anatomy & Physiology
They are composed of groups of individual specialized cells called neurons (or nerve cells), which transmit motor and sensory information back and forth between the PNS and central nervous system (CNS). Transmission is initiated via electrochemical impulses known as action potentials. By definition, nerves are bundles of axons (or nerve fibers.
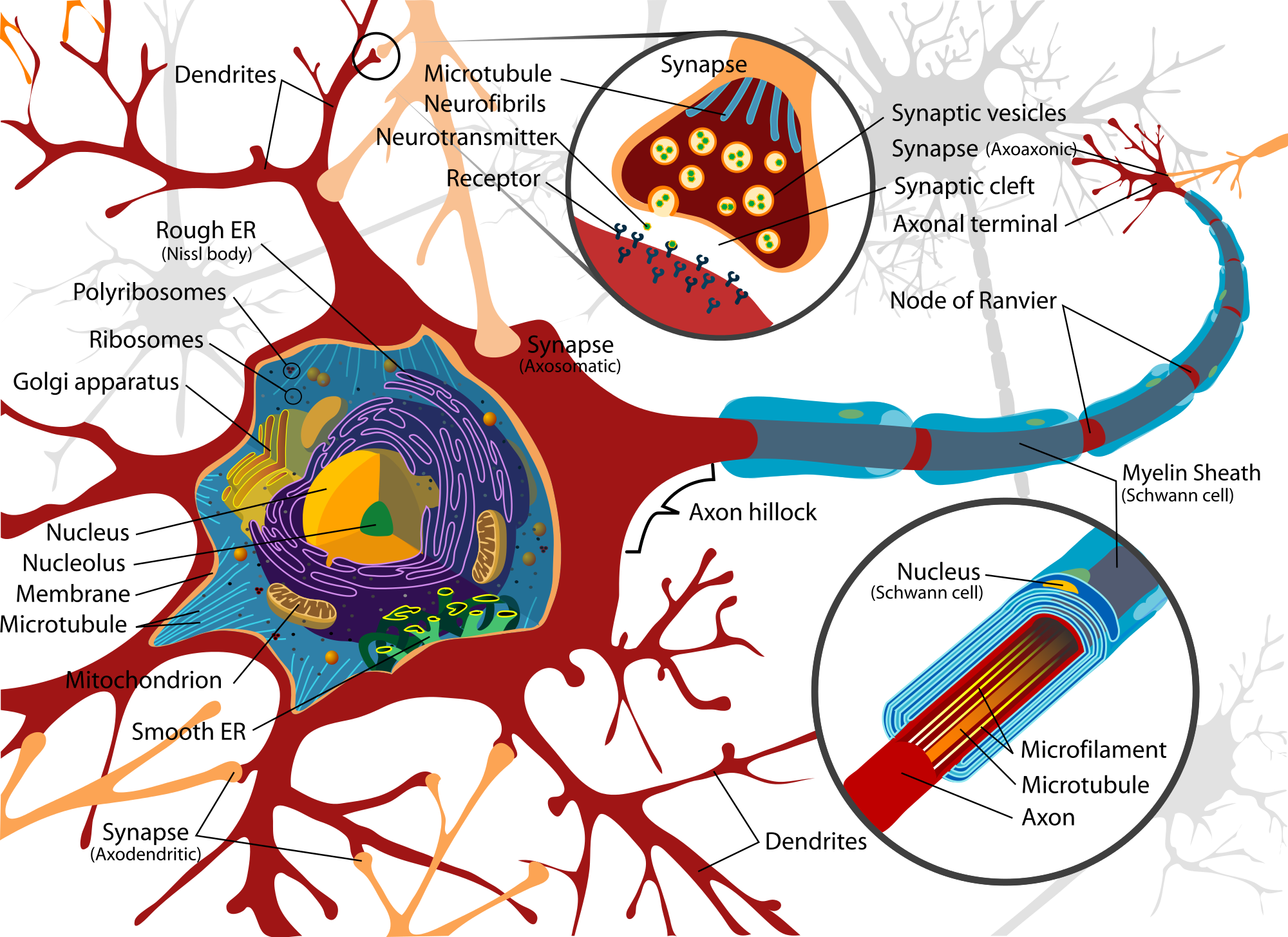
Nerve Cell Diagram Labeled ClipArt Best
The CNS consists of the brain and spinal cord and controls virtually every function of our bodies and minds, including our movements, thoughts, emotions, desires, hormonal fluctuations, breathing, heart rate, and more. The PNS is made up of nerves that branch off from the spinal cord and extend to all other parts of the body.

Nerve cells Mayo Clinic
The membranes of these cells consist of a fat (lipoprotein) called myelin. The membranes are wrapped tightly around the axon, forming a multilayered sheath. This myelin sheath resembles insulation, such as that around an electrical wire. Nerve impulses travel much faster in nerves with a myelin sheath than in those without one.

Human neuron structure nerve cell medical chart Vector Image
neurons . They are adapted to carry electrical impulses from one place to another. They feature: an axon - a single nerve fibre that carries nerve impulses away from a cell body which is.
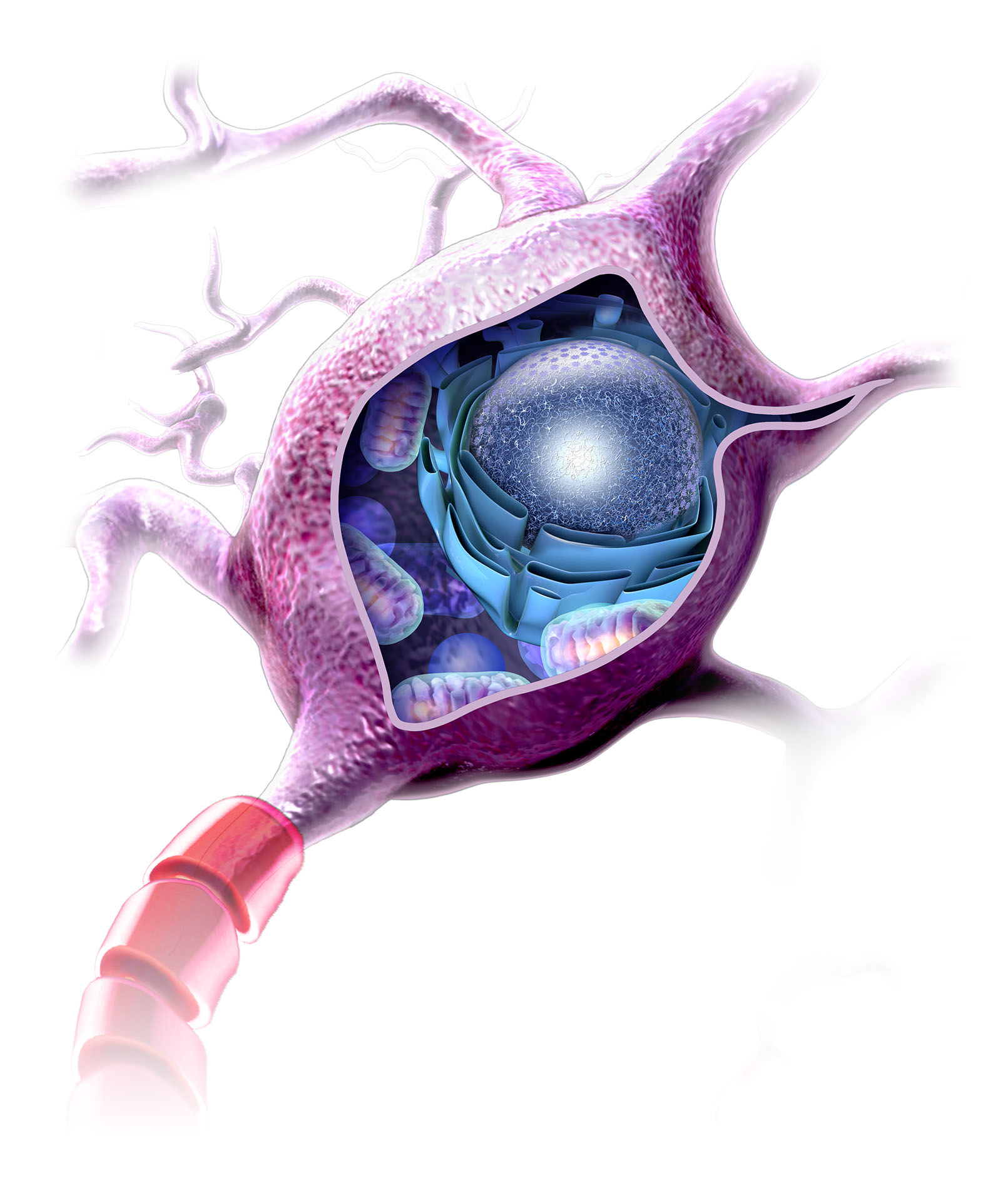
Nerve Cell Internal Structure Portfolio SayoStudio
Overview What are nerves? Nerves are like cables that carry electrical impulses between your brain and the rest of your body. These impulses help you feel sensations and move your muscles. They also maintain certain autonomic functions like breathing, sweating or digesting food. Nerve cells are also called neurons.

Nerve Cell The Definitive Guide Biology Dictionary
Cell body Also known as a soma, the cell body is the core section of the neuron. The cell body contains genetic information, maintains the neuron's structure, and provides energy to drive.
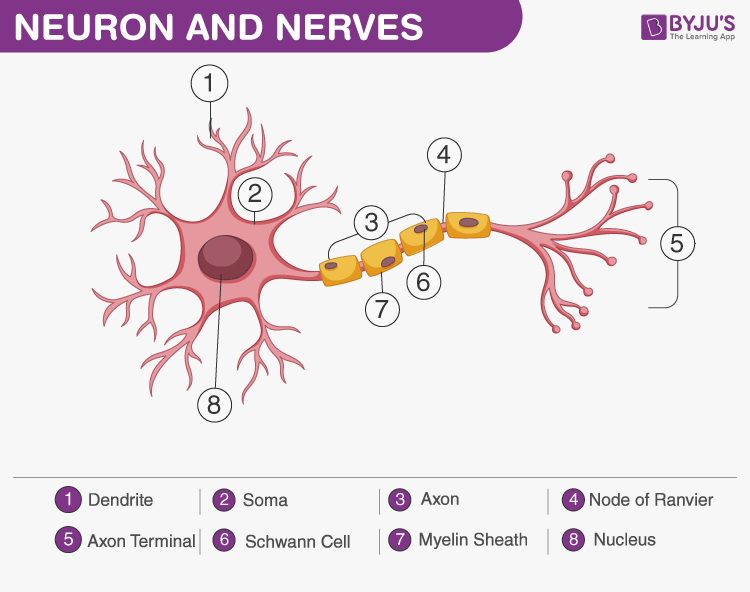
What Is A Nerve? Structure, Function, Types of Nerves, Nerve Disorders
Diagram Of Neuron with Labels Here is the description of human neuron along with the diagram of the neuron and their parts. The neuron is a specialized and individual cell, which is also known as the nerve cell. A group of neurons forms a nerve.