
Boerhaave syndrome Radiology Case
Boerhaave syndrome is spontaneous esophageal rupture from forceful vomiting. After initial concerns for the pneumomediastinum secondary to perforation esophageal malignancy, this case was given the clinical diagnosis of Boerhaave syndrome. 2 articles feature images from this case 41 public playlists include this case Related Radiopaedia articles
Boerhaave Syndrome Radiology Key
Boerhaave's syndrome is a rare form of esophageal perforation with a potentially complex presentation mimicking a variety of disorders. The prompt radiologic evaluation utilizing plain films, computed tomography and fluoroscopic esophagrams may avert the serious complications associated with a delay in diagnosis and treatment.
Boerhaave Syndrome and MalloryWeiss Syndrome (MWS) Lecturio
Boerhaave Syndrome: To Treat or Not to Treat by Means of Insertion of a Metallic Stent. Journal of Vascular and Interventional Radiology 6:5, 741-743. [Crossref] DC Cameron, J Black. 1995. Lightweight suction drainage - feeding system for oesophagogastric anastomotic leaks. Australasian Radiology 39:3, 314-319. [Crossref]

Acute Respiratory Failure in a Patient With Spontaneous Esophageal Rupture (Boerhaave Syndrome
Boerhaave syndrome represents the clinical syndrome associated with spontaneous esophageal rupture from retching and vomiting. The factor most often associated with a high mortality is a delay in diagnosis as this can result in significant mediastinal infection and tissue destruction [1-3]. Surgical repair remains the mainstay of therapy.

Boerhaave syndrome Radiology Case Radiology, Syndrome, Medicine
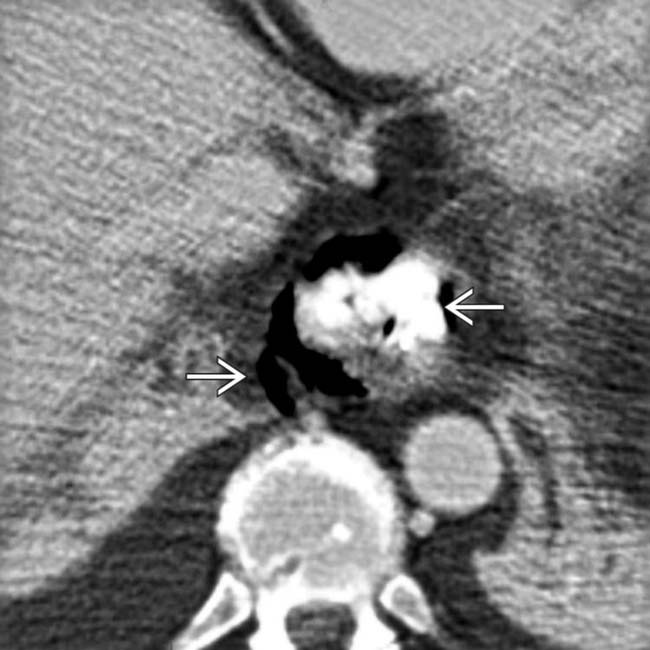
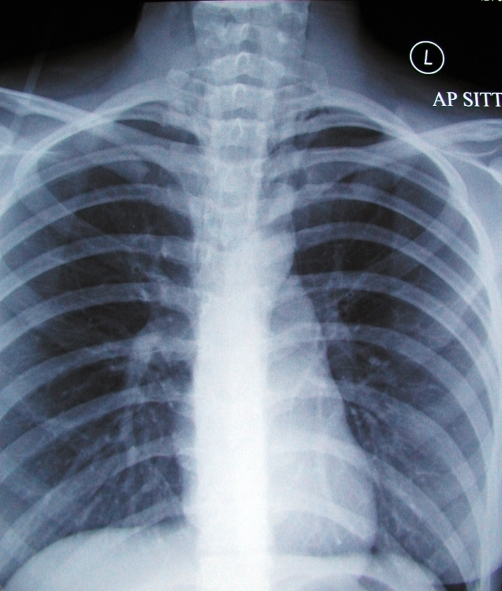
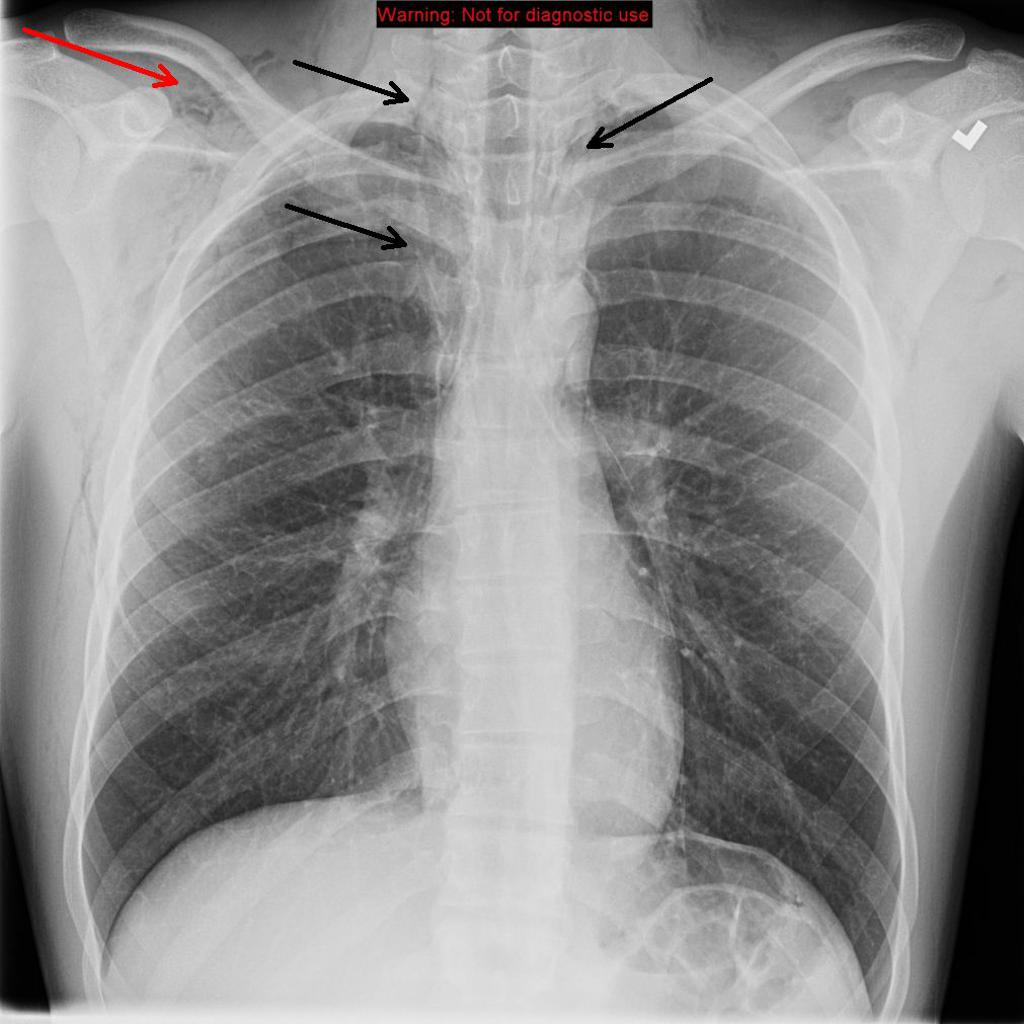
Age: 35 years Gender: Male x-ray There is a veiling opacity over the left hemithorax, likely from pleural fluid on the supine film. There is a retrocardiac opacity that obscures the diaphragmatic silhouette, indicating left lower lobe consolidation. ct Axial C+ arterial phase Axial lung window Coronal C+ arterial phase
Boerhaave syndrome chest x ray wikidoc
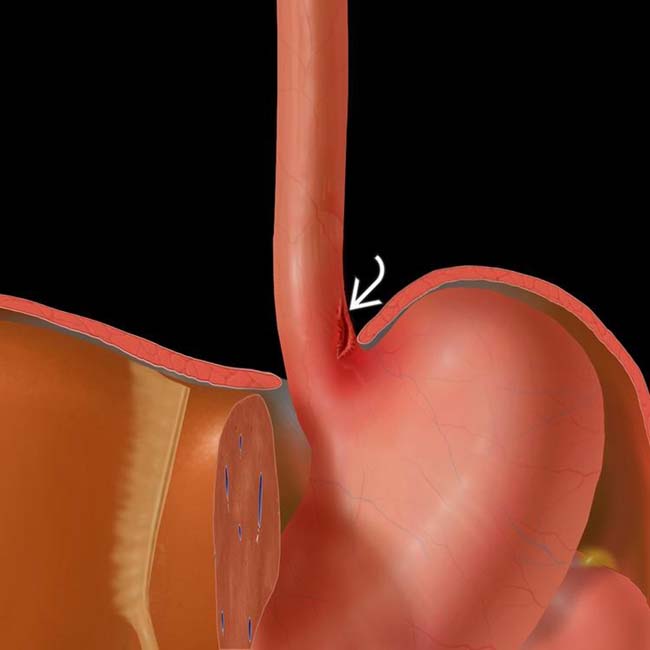
Boerhaave's syndrome is the spontaneous rupture of the esophagus, which requires early diagnosis and treatment. Symptoms may vary, and diagnosis can be challenging. Case 1: A 54-year-old Chinese man presented to us with sudden-onset epigastric pain radiating to the back following hematemesis. Upper gastrointestinal endoscopy revealed a full-thickness rupture of the esophageal wall.
Boerhaave Syndrome Radiology Key
The aim was to define the diagnostic value of chest radiography, esophagography, and computed tomography (CT) in patients with Boerhaave's syndrome.

Boerhaave Syndrome Radiology Key
Boerhaave syndrome is a transmural perforation of the esophagus and should be distinguished from Mallory-Weiss syndrome, a nontransmural esophageal tear also associated with vomiting.. Radiology case reports. 2018 Oct:13(5):1084-1086. doi: 10.1016/j.radcr.2018.04.026. Epub 2018 May 19 [PubMed PMID: 30228849] Level 3 (low-level) evidence.

Boerhaave syndrome Radiology Case
Boerhaave's syndrome is a spontaneous rupture of the esophagus that occurs during intense straining. It most typically occurs during an episode of forceful or repeated vomiting. When the esophagus tears, toxic contents can leak out and cause infection. This is an emergency. Without treatment, it can be fatal within days.

Boerhaave Syndrome Radiology Key
Emergency Radiology; Expert Panel Narrative Reviews; Global Reading Room; Journal Club; Noninterpretive Skills; Photon-Counting Detector CT; Point/Counterpoint; Special Series Review; Information. About AJR; Editorial Board;. Boerhaave syndrome: interventional radiologic management.

Cureus Atypical Presentation of Boerhaave Syndrome With Hypoxia and Unresponsiveness
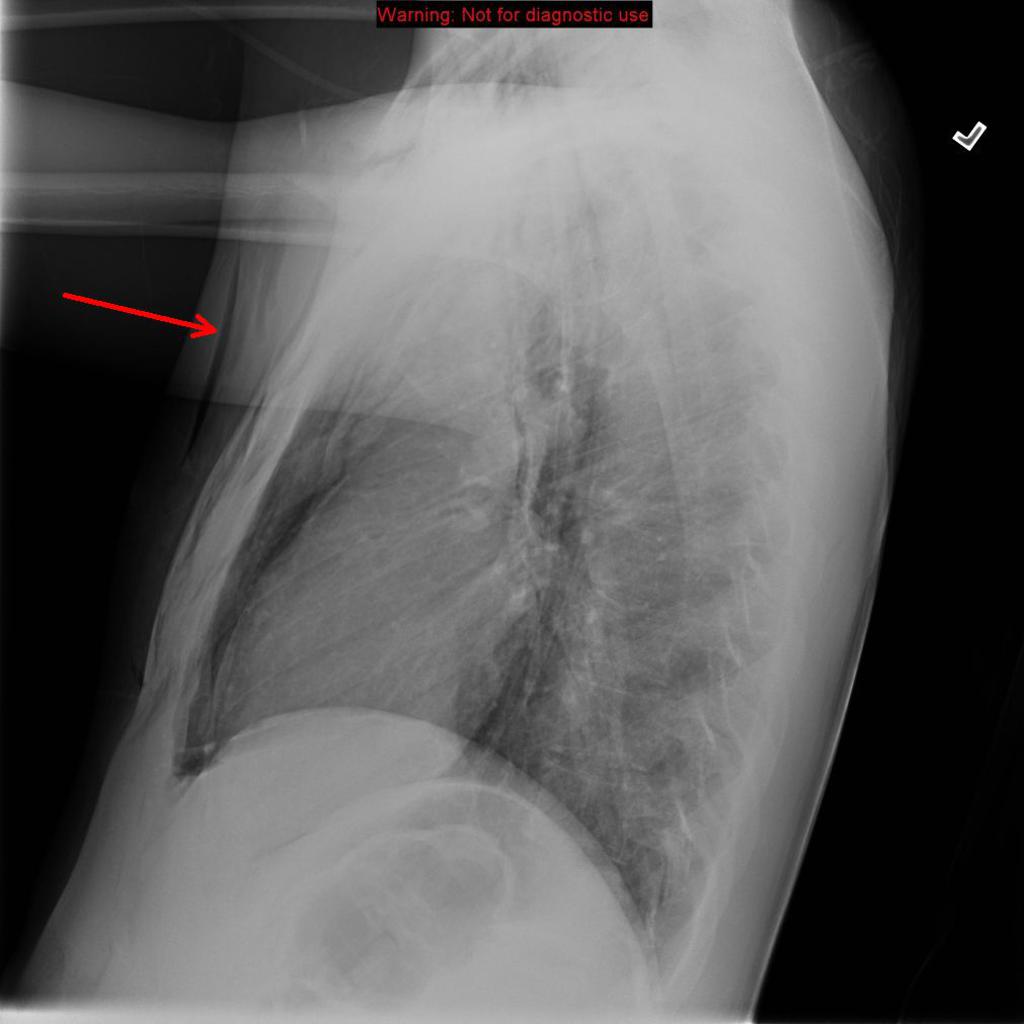
In spontaneous esophageal rupture (Boerhaave's syndrome), the diagnostic radiological finding is the V sign of Naclerio ( Figure 1 ), identified on a chest X-ray as two hypertransparent V-shaped lines, one along the left border of the aorta and the other creating the continuous diaphragm sign on the left.

SciELO Brasil Boerhaave’s syndrome the role of conventional chest Xray Boerhaave’s
Boerhaave syndrome is a barogenic injury resulting from a sudden increase in intraluminal pressure against a closed cricopharyngeus. Neuromuscular dysfunction results in a non-relaxed cricopharyngeus with a resultant rise in pressure.
Boerhaave syndrome chest x ray wikidoc
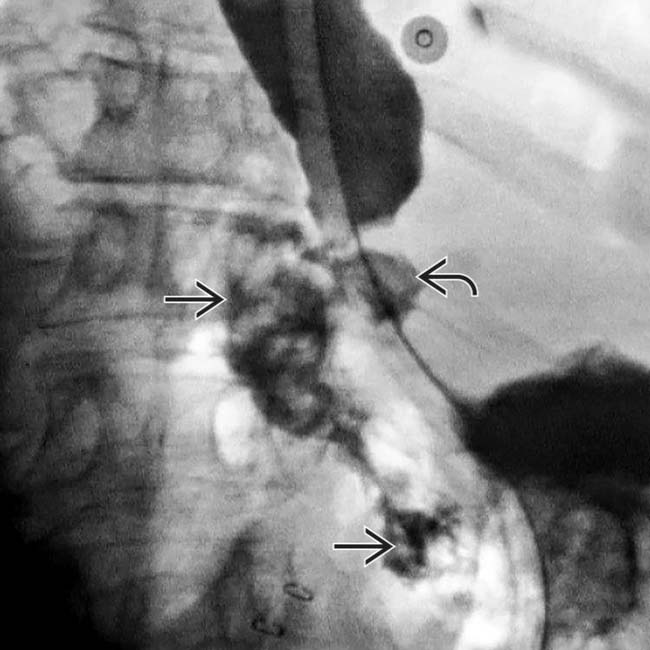
General Features. • Best diagnostic clue. Extraluminal gas and contrast material in lower mediastinum surrounding esophagus. • Other general features. Sudden increase in intraluminal pressure leads to full-thickness esophageal perforation. Left side of distal thoracic esophagus. - Most vulnerable (due to lack of supporting mediastinal.
Boerhaave Syndrome Radiology Key
Causes of esophageal injury include iatrogenic (including esophagogastroduodenoscopy and stent placement), foreign body ingestion, blunt or penetrating trauma to the chest or abdomen, and forceful retching, also called Boerhaave syndrome.

Edinburgh Emergency Medicine Boerhaave Syndrome
Boerhaave syndrome refers to an esophageal rupture secondary to forceful vomiting and retching. Epidemiology It tends to be more prevalent in males, with alcoholism a risk factor. The estimated incidence is ~ 1:6000. Clinical presentation

Boerhaave syndrome Radiology Case
Spontaneous oesophageal rupture (Boerhaave's syndrome) is an uncommon but serious condition. A retrospective review was undertaken of the management of 34 patients (age range 17-85 years) presenting between 1991 and 2006. Contrast swallow was possible in 22 patients, confirming the diagnosis in 17.