Cardiovascular System5
Circulatory adjustments are effected by altering the output of the pump (the heart), changing the diameter of the resistance vessels (primarily the arterioles), or altering the amount of blood pooled in the capacitance vessels (the veins). Regulation of cardiac output is discussed in Chapter 30. This chapter reviews the systemic regulatory.

What Is a Healthy Resting Heart Rate? UPMC HealthBeat Normal heart rate, Heart rate, Normal
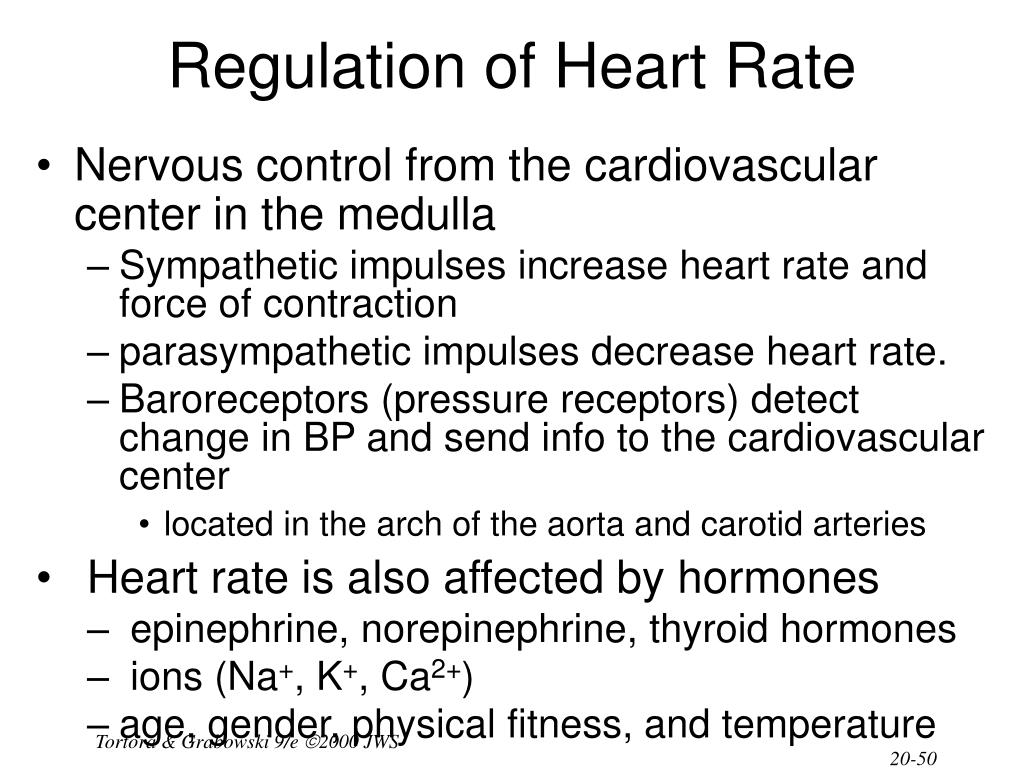
The cardiac cycle is a normal activity of the human heart and is regulated automatically by the nodal tissues- the sinoatrial node (SA node) and atrioventricular node (AV node). The variation in the cardiac cycle results in an increase or decrease in cardiac output.

PPT The Cardiovascular System The Heart PowerPoint Presentation, free download ID6725545
6. Maximum Heart Rate (MHR) - age related number of BPM of the heart when working at maximum MHR= 220 - Age Knowing this number along with RHR allows you to find the correct intensity for your body when being physically active. Low intensity, closer to RHR High intensity, closer to MHR Given this information, where do you think HR shou.

Regulation of heart rate (Cardiovascular variables part 2) YouTube
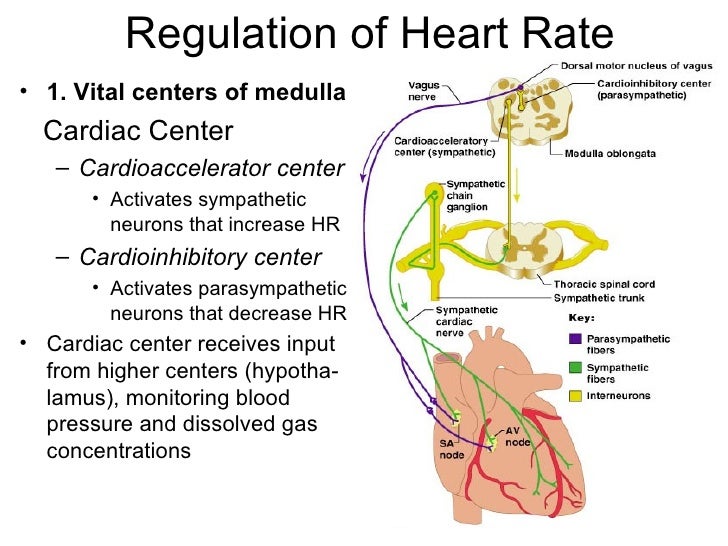
Control of Cardiac Activity. CARDIAC OUTPUT = HEART RATE X STROKE VOLUME. Pacemaker Activity. Myocardial Performance. TWO POINTS TO REGULATE. EXTRINSIC REGULATION. Download Presentation respiratory regulation control regulation overview vs baroreceptor reflexes force development intrinsic regulationof hazelle Download Presentation
Regulation of Heart Function
Answers • 1. You need a heart to pump blood. • 2. You need blood to circulate to all the parts of your body in order for oxygen to get to all body cells (gas exchange) • Oxygen/ Carbon Dioxide exchange Introduction • How does your heart pump blood?

Fetal Heart Rate Physiology and its control with EFM
Heart Rate and its Regulation (With Diagram) Article Shared by ADVERTISEMENTS: Normal heart rate is about 60-90 beats per minute. On an average, the rate at which the heart beats is about 75 per minute. It depends on the balanced activity between the sympathetic and parasympathetic nerve influence that are acting on it.

Regulation of Heart Rate YouTube
A normal resting heart rate ranges from 60-100 beats per minute (bpm). Resting rates higher than 100 bpm suggest that the heart is working too hard to circulate blood, and thus may indicate a serious problem that should be monitored by a physician. Resting rates lower than 60 bpm occur more often with endurance-trained athletes whose bodies are.

PPT Chapter 18 The Heart and Cardiovascular Function Lecture 3 PowerPoint Presentation ID
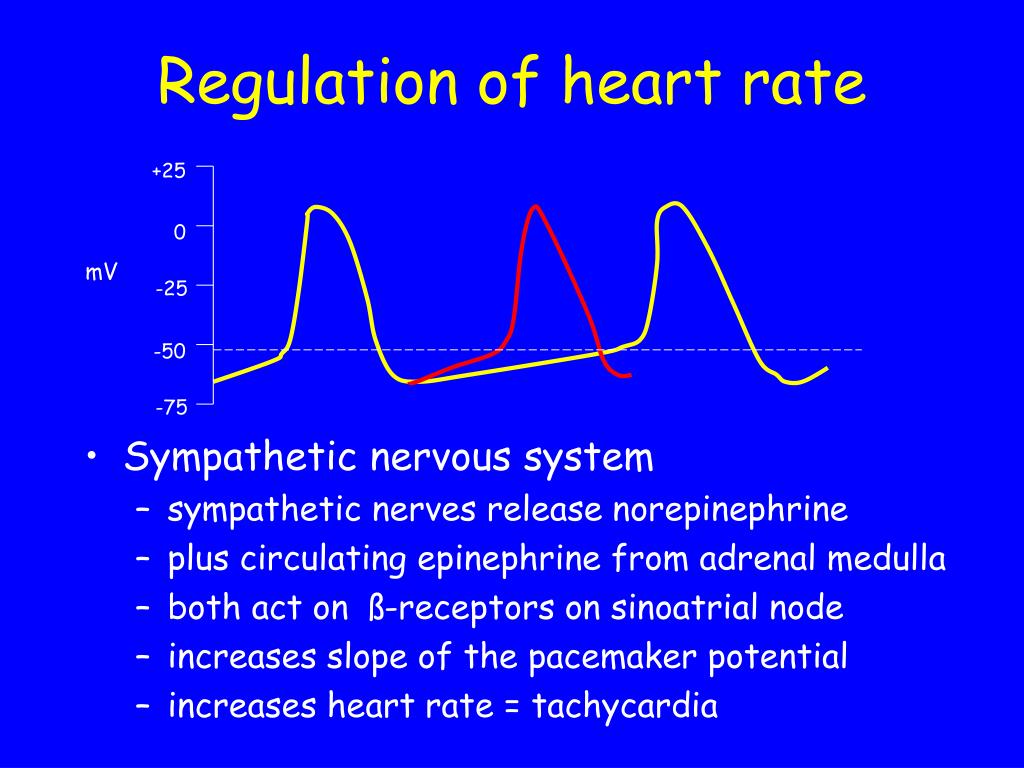
Regulation of Heart Rate - Free download as Powerpoint Presentation (.ppt), PDF File (.pdf), Text File (.txt) or view presentation slides online. SINUS ARRHYTHMIA There is a change in HR seen during respiratory cycle in inspiration, there is increase in HR In expiration, there is decrease in HR It is commonly seen in children and young adults.
PPT Regulation of stroke volume & heart rate PowerPoint Presentation ID3097878
Whereas in hormonal regulation, hormones like catecholamine, acetylcholine regulates the heart rate. Other factors like environment stress, drugs also regulate the heartbeat. Cardio-vascular system is not only associated with circulation of blood, but also with certain CVDs like, heart attack, hypertension, cardiomypathy, congenital heart.
PPT Chapter 20 The Cardiovascular System The Heart PowerPoint Presentation ID311973
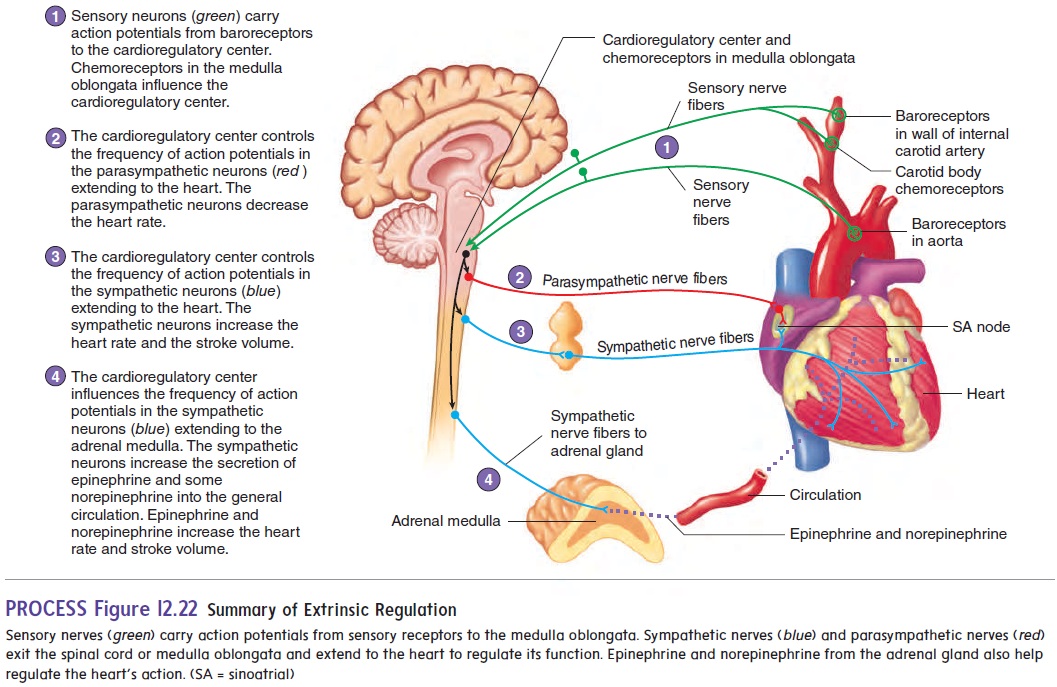
There are two primary modes by which the blood volume pumped by the heart, at any given moment, is regulated: 1) intrinsic cardiac regulation, in response to changes in the volume of blood flowing into the heart; and 2) control of heart rate and cardiac contractility by the autonomic nervous system. The intrinsic ability of the heart to adapt.

A simplified schematic for the mechanism of heart rate regulation by... Download Scientific
Intrinsic Regulation • Depolarization muscle membrane creates an action potential or electrical impulse • Impulse travels through the heart in an established pathway • SA node →across atria →AV node →AV bundle →left & right bundle branches → Purkinjie fibers → Ventricles

Heart rate regulation Neural, Hormonal and Intrinsic YouTube
Cardiac regulation is constantly working to ensure sufficient blood flow supply is sent around the body. When we exercise, we increase cardiac output so our muscles can get the oxygen they need. When we sleep, cardiac output is decreased as our body is resting. This section will explore the various regulated variables that influence cardiac.
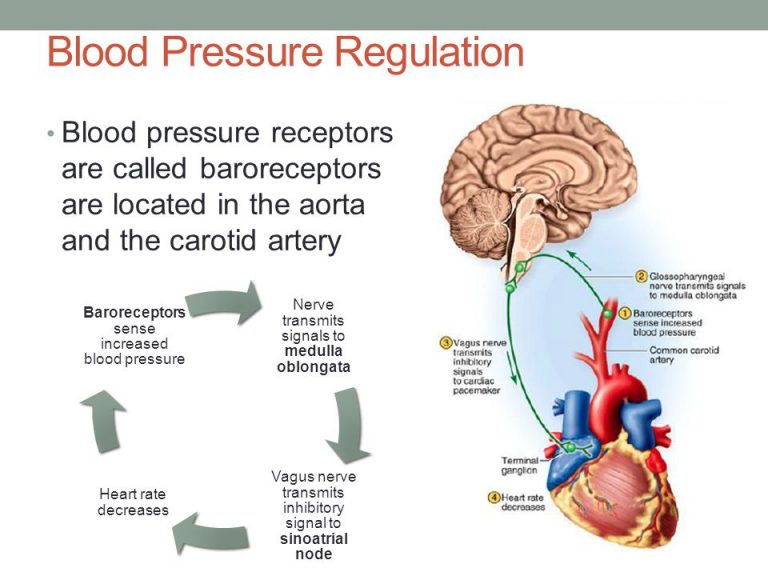
Cardiovascular system, Blood pressure regulation, Heart rate & its regulation Science online
The body's nervous system, neurotransmitters and hormones regulate the sinus node and play a huge role in how the body regulates heart rate. Each contraction of the heart muscle regulates the flow of blood in the form of a pulse or heart rate. The pulse is measured in beats per minute. Emotional and physical stress, exercise and other physical.
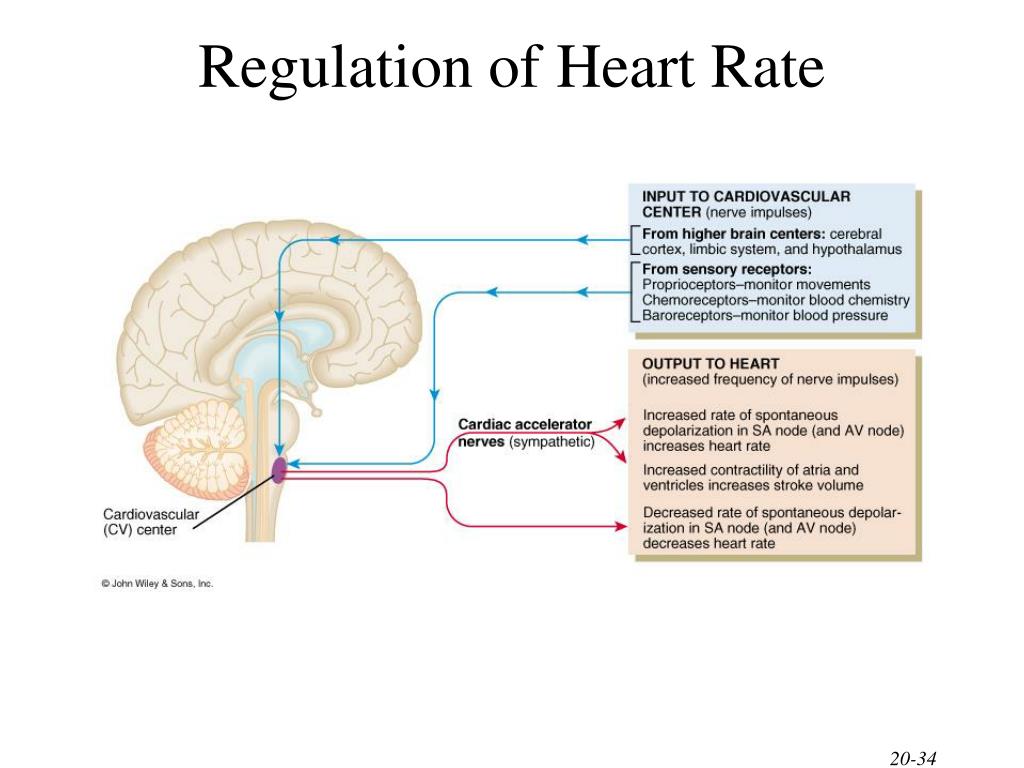
PPT The Cardiovascular System The Heart PowerPoint Presentation, free download ID1797476
Section Four Cardiovascular Regulatory Mechanisms • Nervous Regulation • Humoral Regulation • Local control of blood flow. I. Nervous Regulation (I) Innervation of the heart and blood vessels. Right side Left side Heart rate Myocardial contractility. Right side Left side Heart rate Conductivity. NE+ß1R Ach+N1R Stellate ganglion Cervical sympathetic ganglia Heart T1-T5 thoracic spinal.
ATW's Guide To Lowering Your Heart Rate
1. Nervous System controlling Heart Rate The heart rate is therefore determined by the balance between sympathetic and parasympathetic nerve activity The cardiovascular centre receives input from 4 main receptor groups, these inputs are processed and the sympathetic/ parasympathetic NS is recruited accordingly.
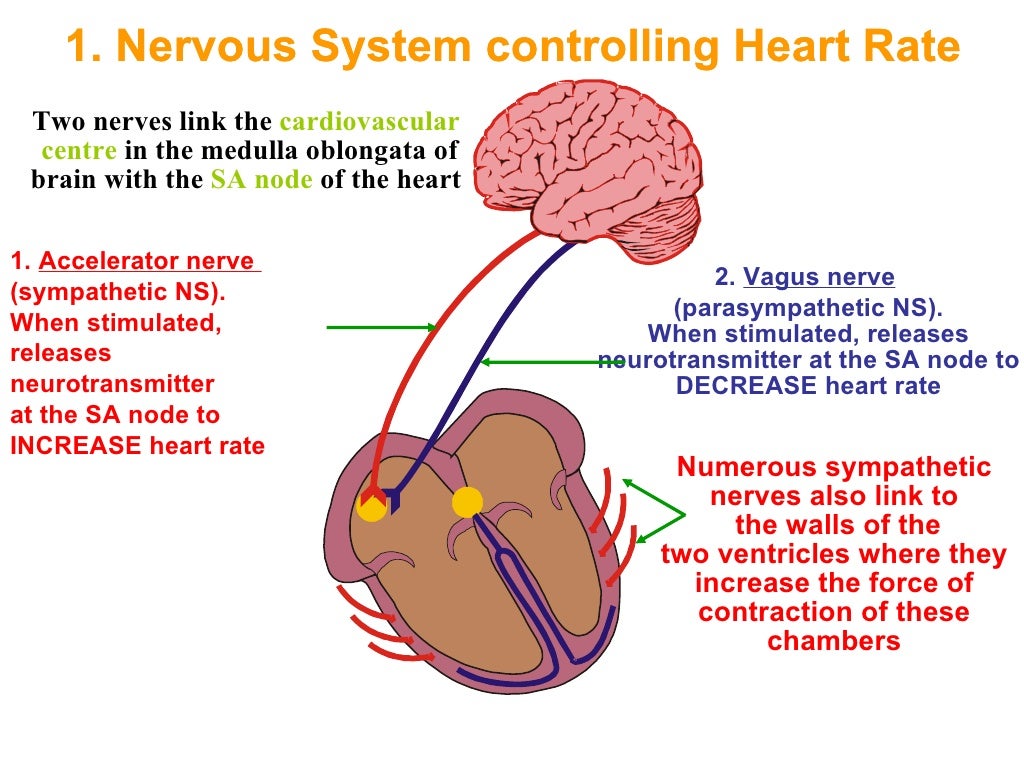
Control of heart rate
2. -Heart rate, or heart pulse, is the speed of the heartbeat measured by the number of poundings of the heart per unit of time — typically beats per minute (bpm). The heart rate can vary according to the body's physical needs, including the need to absorb oxygen and excrete carbon dioxide. Activities that can provoke change include physical.