
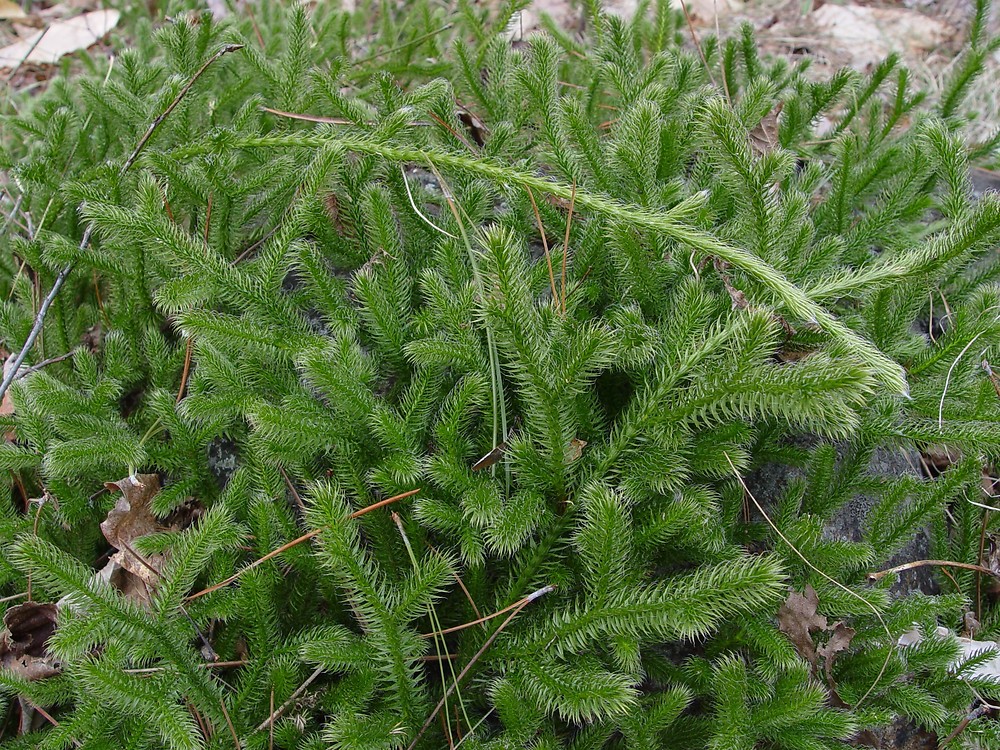
Lycopodium obscurum or L. hickeyi (Pennsylvania clubmoss, … Flickr
Lycophyte sporangia are stalked and kidney-shaped, as in the zosterophyllophytes. In the earliest lycophyte groups, such as the Asteroxylales, the sporangia are oriented across the leaf, so that the widest dimension of the sporangium is perpendicular to the axis of the leaf.

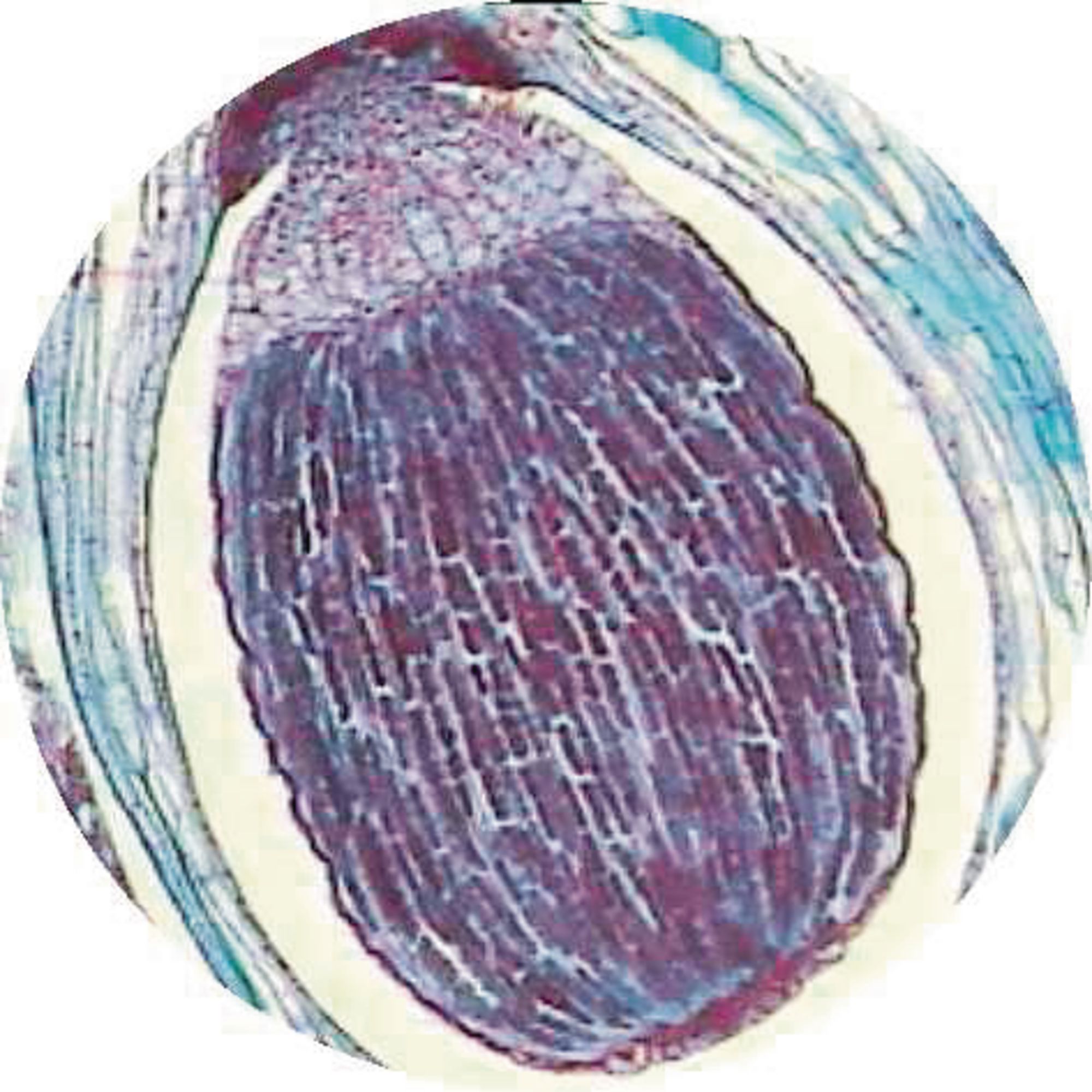
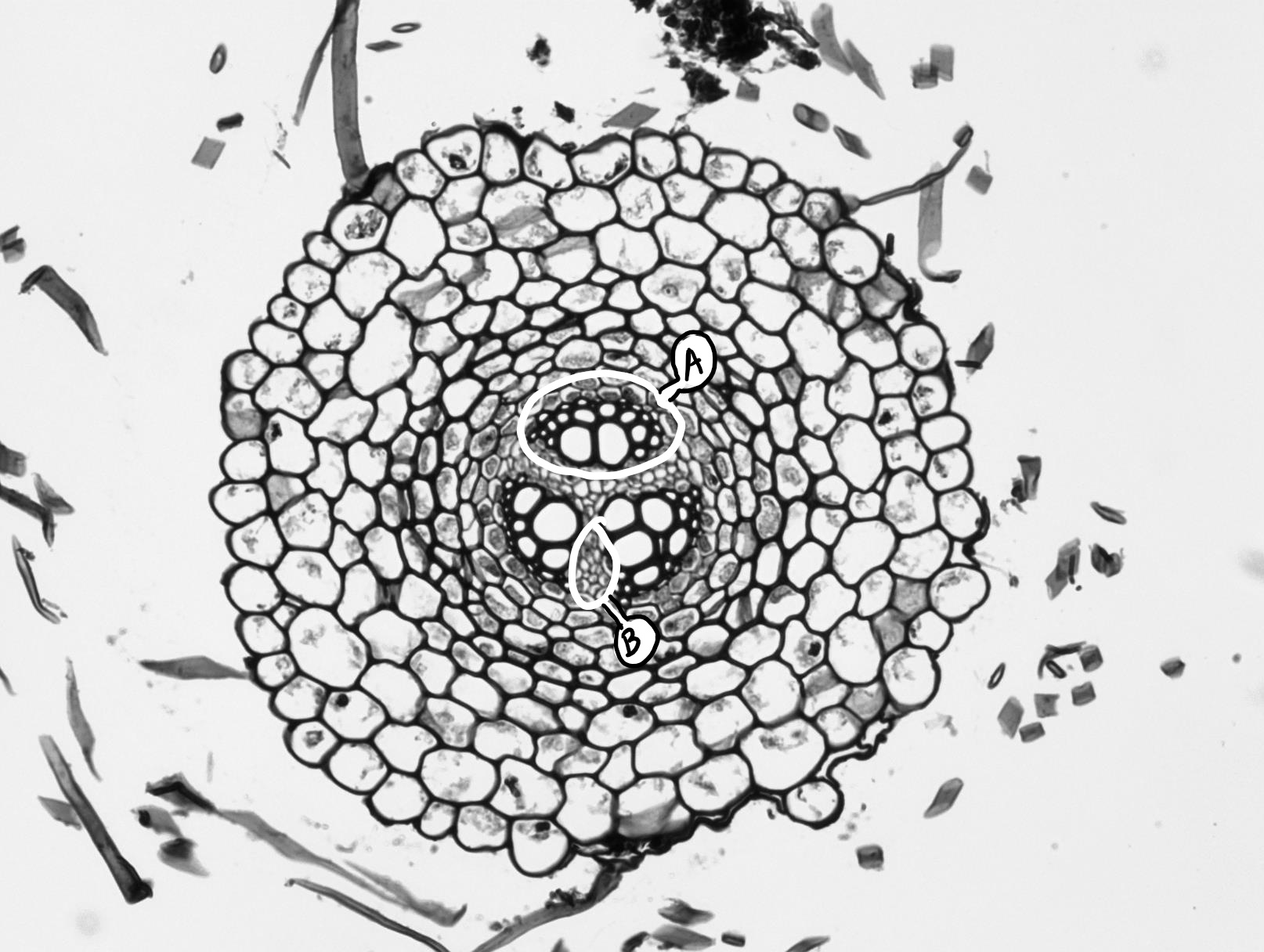
Lycopodium, stem, transverse section, stele
1. Plant body is sporophytic and the sporophyte is divisible into roots, stem and leaves (Fig. 224). 2. The genus is divisible into two subgenera, i.e., Urostachya and Rhopalostachya.

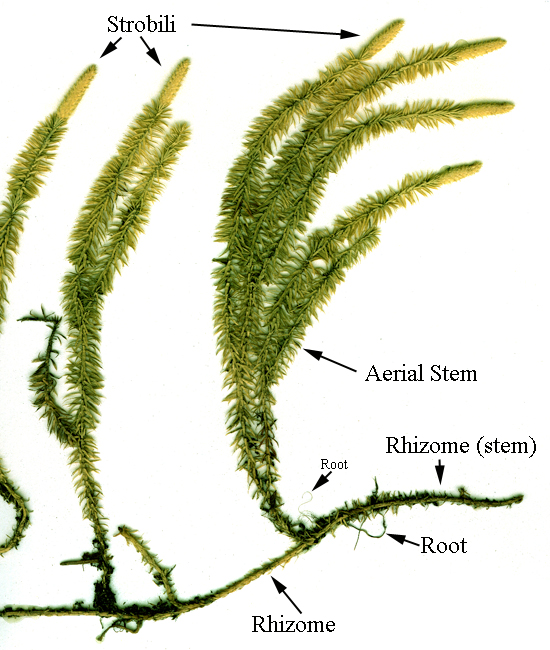
Strobilus on a Lycopodium. This is on the top of the stem typically, or found branched elsewhere
In this article we will discuss about the anatomy of lycopodium. Also study the strobilus, arrangement of sporangia, L.S. strobilus and spores of lycopodium. Cut thin transverse sections of stem, leaf and root by inserting the material in pith, stain in safranin- fast green combination, mount in glycerine and study- under microscope.
Whole plant illustrated
In this article we will discuss about the structure of Lycopodium with the help of diagrams. The main plant body is sporophytic. It consists of slender and branched stem, numerous small leaves (microphylls) and dichotomously- branched roots (Fig. 7.23A, B). Roots: The primary root or first formed root of the young sporophyte is ephemeral, short-lived. The older plants have dichotomously.
Lycopodium T.S. Stem. B8A10984 Philip Harris
2. Cortex: 3 layers in L.cerenuum 3. Outer and inner cortex is parenchymatous and middle cortex is sclerenchymatous 4. Endodermis: single layered, often with casparian thickening 5. Pericycle: One to many layered made up of parenchymatous cells 6. Stele: basically protostele Varies in different species:
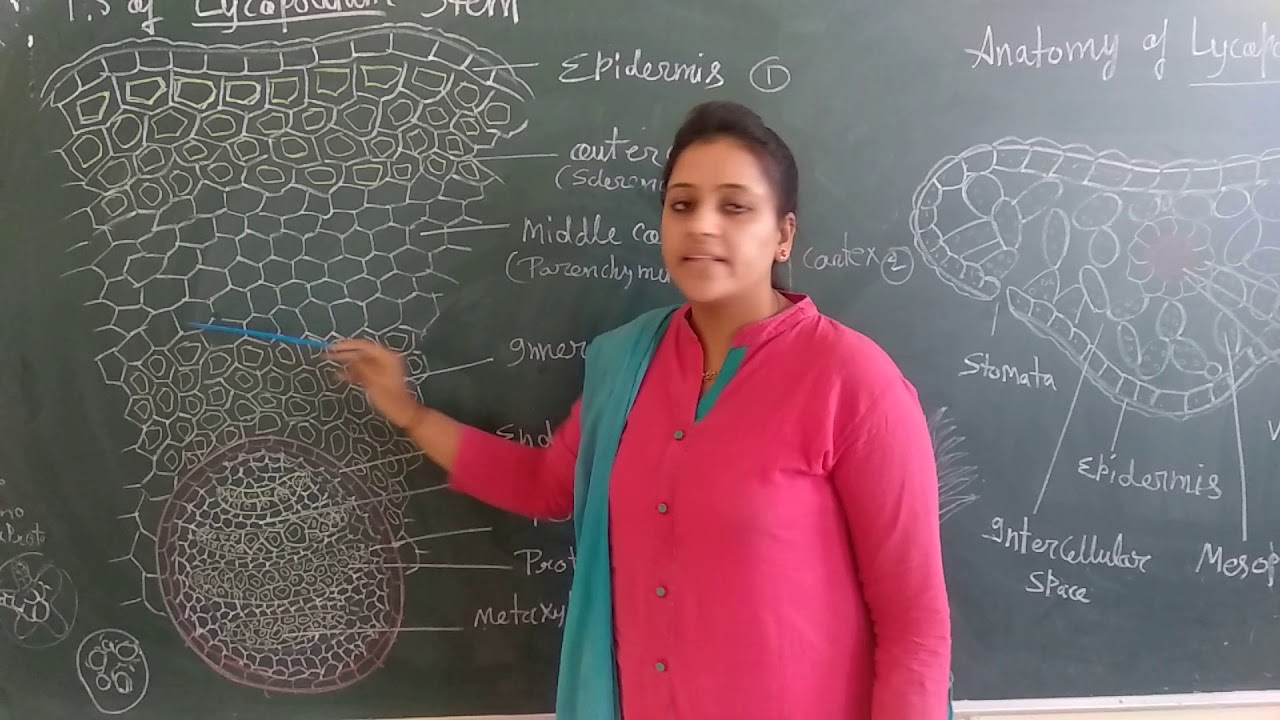

Lycopodium stem (Anatomy) YouTube
Asexual propogation of sporophytes can occur via an underground stem that travels horizontally, called a rhizome. Figure 2.5.3.1.3 2.5.3.1. 3: A Lycopodium sporophyte growing vegetatively. The branches occur in Y-formations, showing dichotomous branching. There are many small, thin leaves (microphylls).
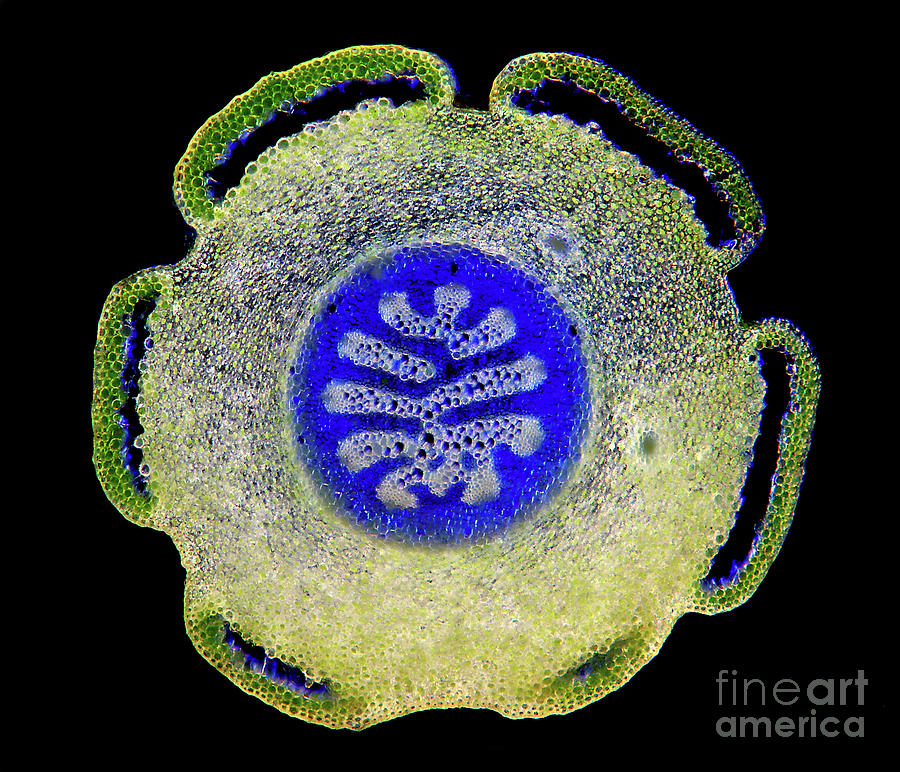
Clubmoss (lycopodium Sp.) Stem Photograph by Marek Mis/science Photo Library
ADVERTISEMENTS: In this article we will discuss about the structure of Lycopodium with the help of diagrams. The main plant body is sporophytic. It consists of slender and branched stem, numerous small leaves (microphylls) and dichotomously- branched roots (Fig. 7.23A, B). Roots: ADVERTISEMENTS: The primary root or first formed root of the young sporophyte is […]

Lycopodium clavatum clubmoss, running clubmoss) Go Botany
is simply a terminal shoot. The central stem bears leaves each with a sporangium. While observing through a dissecting microscope, pull leaves off the stem using teasing needles. Identify megasporophylls bearing megasporangia and microsporophylls bearing microsporangia. Crush each type of sporangium and compare the relative size of each spore.

Lycopodium Alchetron, The Free Social Encyclopedia
Figure 6.1.1. 1: A preserved Lycopodium gametophyte. The flat thallus extending out to the right is the gametophyte. The sporophyte emerges from its left side, the root system developing downward and shoot system developing upward. This gametophyte would normally be green and photosynthetic, but the pigments were lost in the preservation process.

6.1.1 Lycopodium Biology LibreTexts
Lycopodium is homosporous and the spores are produced within large, short-stalked, reniform to somewhat sub-globose sporangia, borne singly either in the axils or on the stem, a little above the sporophylls.
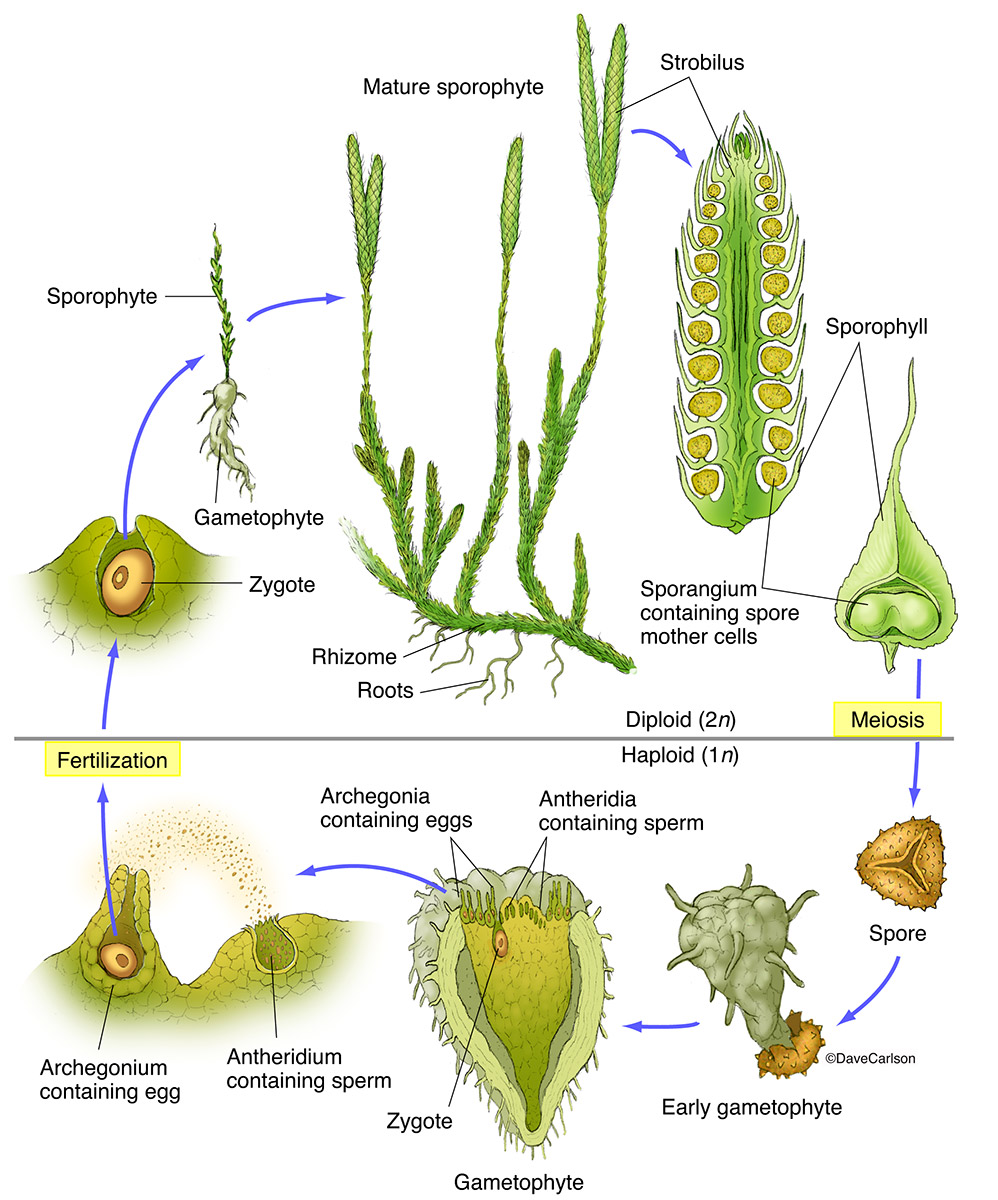
Clubmoss (Lycopodium) Structure & Life Cycle Carlson Stock Art
Anatomy of Stem Anatomy of Root Anatomy of Leaf Lycopodium: Internal and External Structure Systematic Position Division- Pteridophyta Class- Lycopsida Order- Lycopodiales Family- Lycopodiacelae Genus- Lycopodium Distribution and Habitats

LYCOPODIUM CLASSIFICATION, STRUCTURE OF SPOROPHYTE, REPRODUCTION, STRUCTURE OF GAMETOPHYTE AND
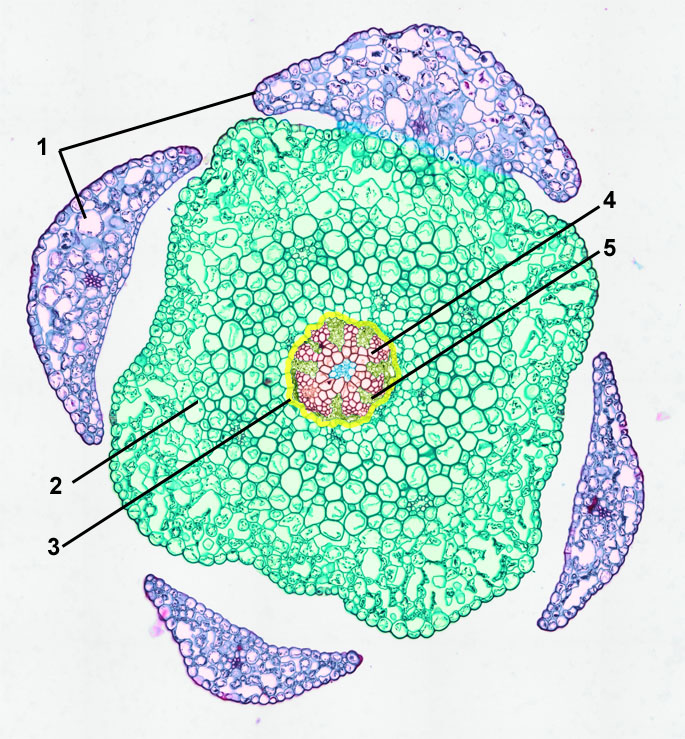
This is a diagram of a section through the node (where the leaf emerges from the stem). The space in the siphonostele is called a leaf gap. It represents where vascular tissue has branched off into the leaf. (b) Dictyostele= with large, overlapping leaf gaps which dissect the vascular system into a network.

LYCOPODIUM CLASSIFICATION, STRUCTURE OF SPOROPHYTE, REPRODUCTION, STRUCTURE OF GAMETOPHYTE AND
Lycopodium (from Greek lykos, wolf and podion, diminutive of pous, foot) [2] is a genus of clubmosses, also known as ground pines or creeping cedars, [3] in the family Lycopodiaceae. Two very different circumscriptions of the genus are in use.
6.1.1 Lycopodium Biology LibreTexts
Stem Leaves Roots Internal Morphology of Lycopodium Anatomy of Stem Epidermis Cortex Stele Anatomy of Root Anatomy of Leaf Reproduction in Lycopodium Vegetative Reproduction Gemmae or Bulbils Fragmentation Resting Buds Root Tubercles Distribution of Lycopodium Lycopodium is a genus of about 400 species.
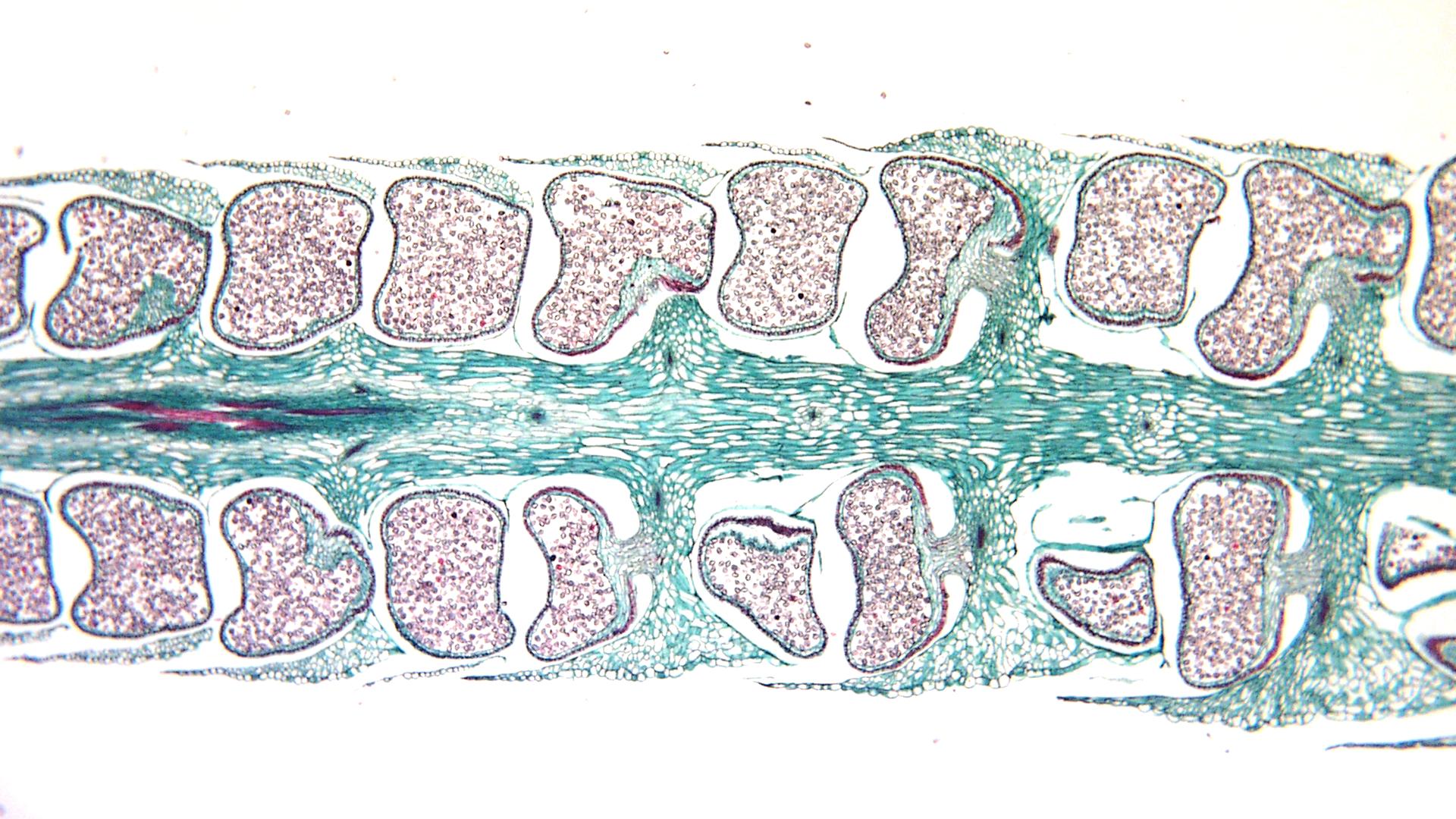
Lycopodium obscurum longitudinal section of strobilus UWDC UWMadison Libraries
The Epidermis of the stem typically has Stomata. The outer Cortex usually contains Chlorenchyma. This photosynthetic tissue may contain a lot of air spaces & can be continuous with the leaves. The take home message is that the stems can make a major contribution to the total amount of photosynthesis that takes place in Lycopodium.
Life cycle of Lycopodium and Selaginella (Spikemoss)
the epidermis (an outermost, protective layer), the vascular cylinder (center for stem support and transport of water, sugars, and nutrients), and the ground tissue, usually parenchyma cells (for storage, including a cortex outside the vascular cylinder and sometimes a pith inside the vascular cylinder). 1. A Lycopodium stem