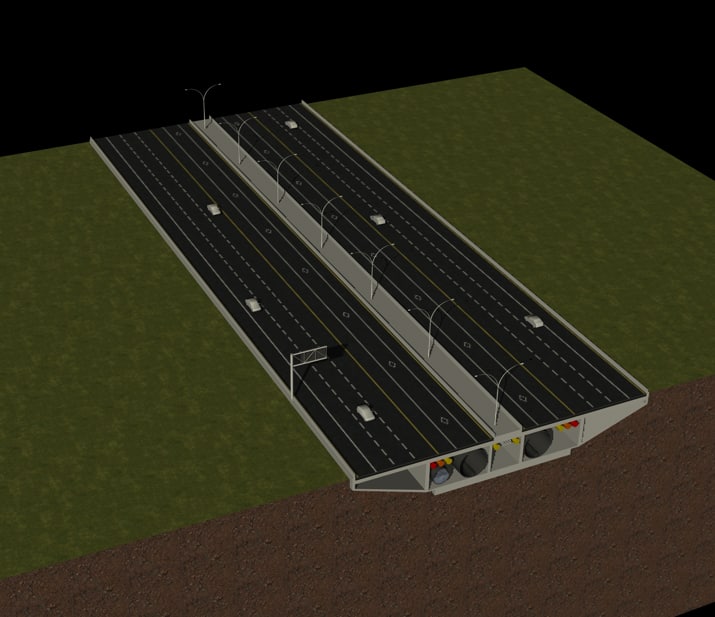

3d model highway cross section
A Policyon Geometric Design of Highways and Streets (also knownas the"Green Book")published by the American Association of State Highway and Transportation Officials (AASHTO) is considered to bethe primary guidancefor U.S. roadway design. For this course, Chapter4 - Cross -Section Elements will beused exclusively for fundamental
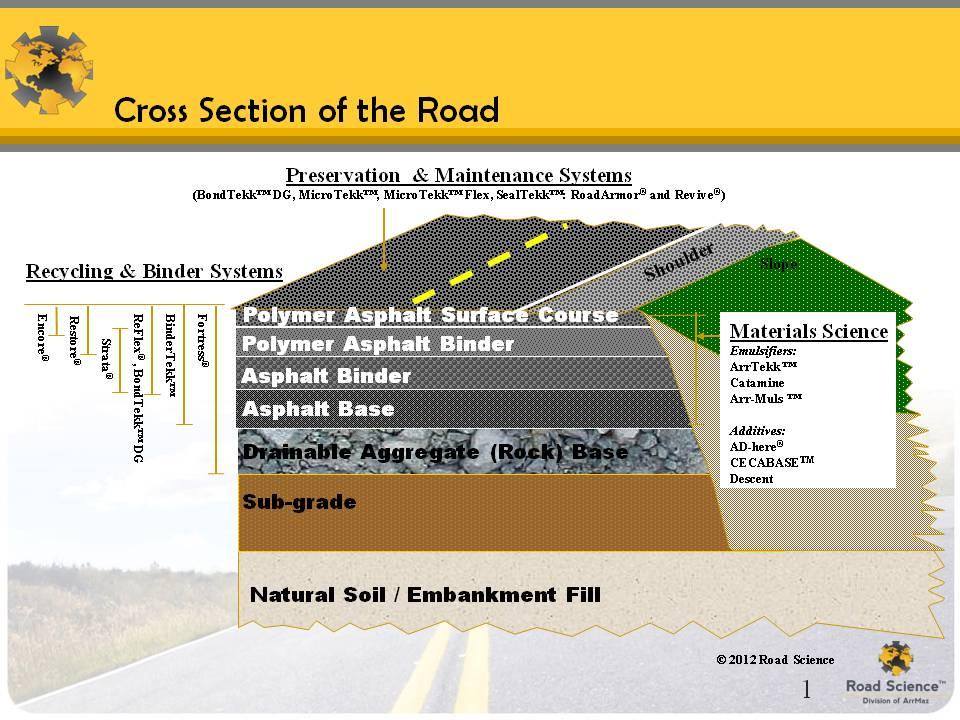
Components Of Road Structure And Method Of Construction Engineering Discoveries
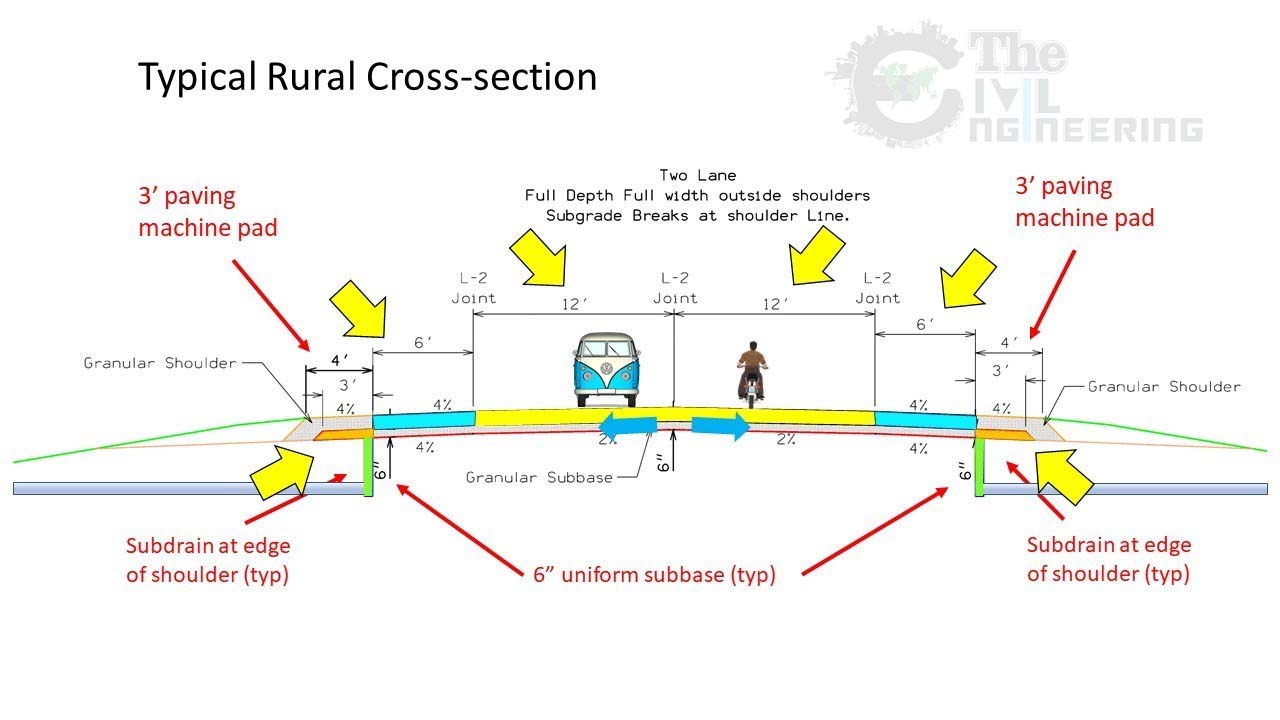
Typical Section with many variations - used on complex projects with multiple templates, along with curb and gutter, and sidewalk. Typical sections show complete geometric information on the roadway cross section from the subgrade up to proposed surface and general information left and right of centerline.

What are the Components of Highways?
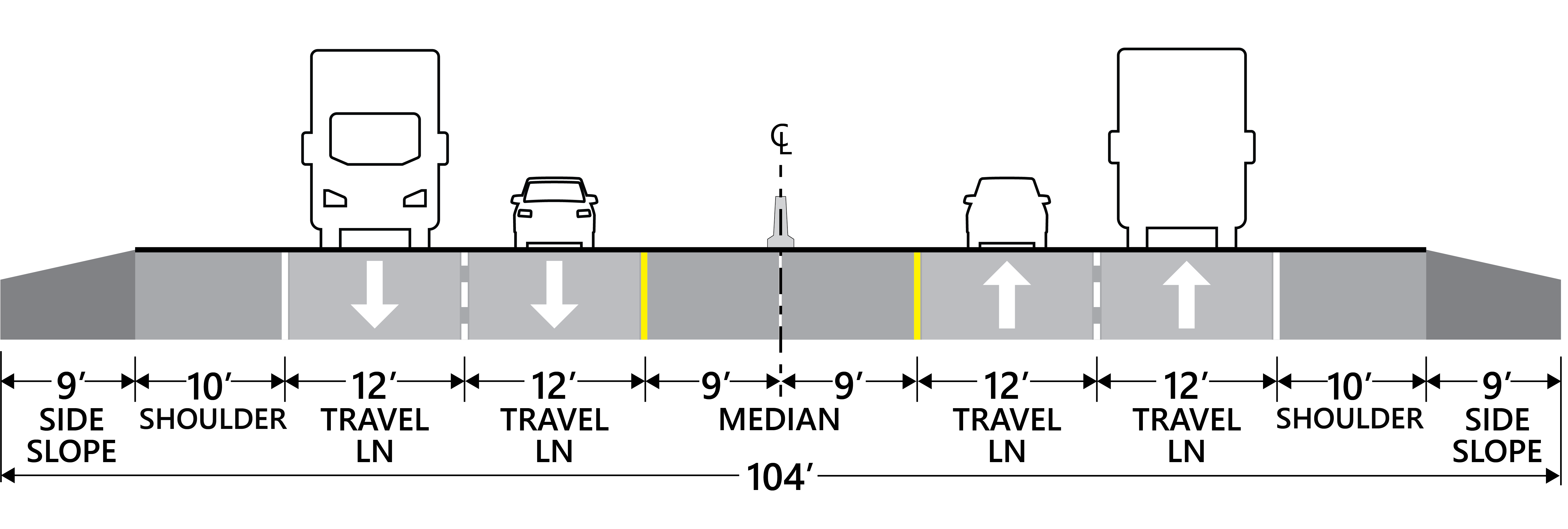
The characteristics of cross-sectional elements are important in highway geometric design because they influence the safety and comfort. The 7 basic cross sectional elements of a highway pavement are. Camber. Width of Carriage way. Kerb.
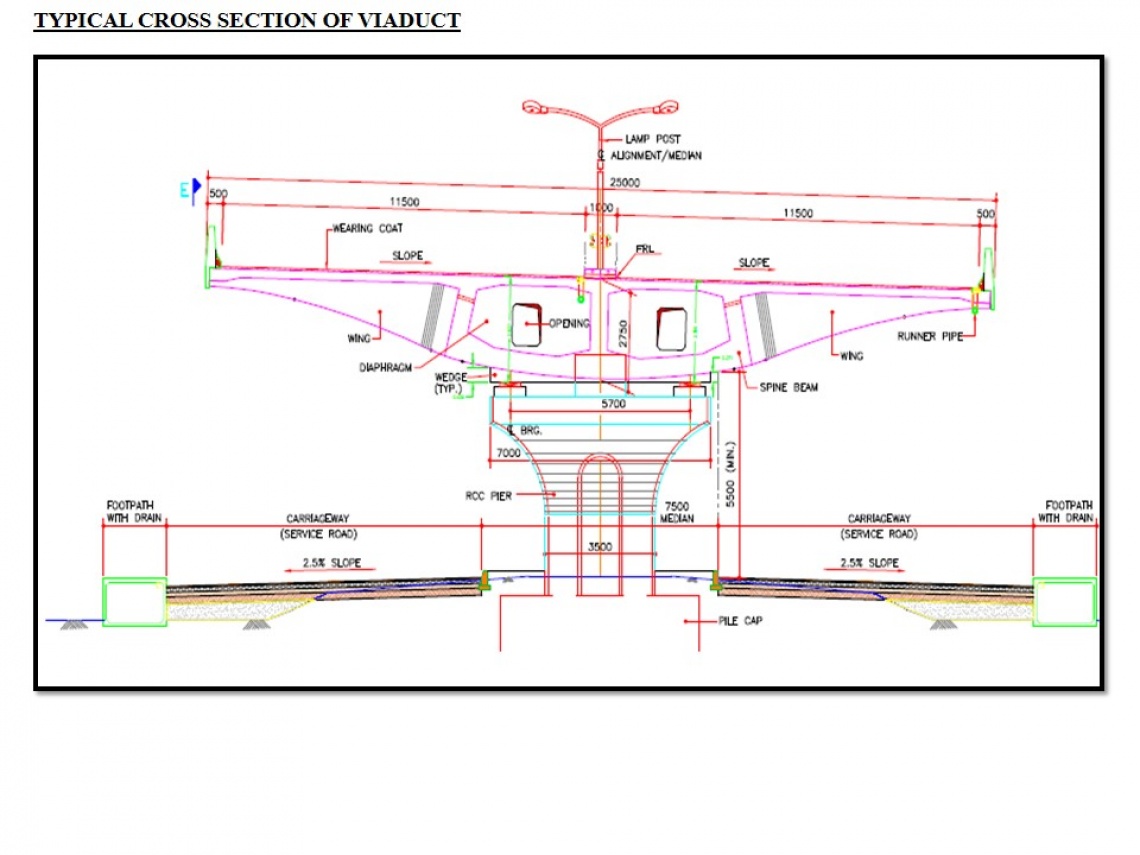
elevated highway CEPT Portfolio
Major Cross Section Elements 5.1 General The major cross section elements considered in the design of streets and highways include the pavement surface type, cross slope, lane widths, shoulders, roadside or border, curbs, sidewalks, driveways, and medians. Due consideration should be given to the motoring and non-motoring users in designing the.
Typical Cross Section Toll Road 01 3D Warehouse
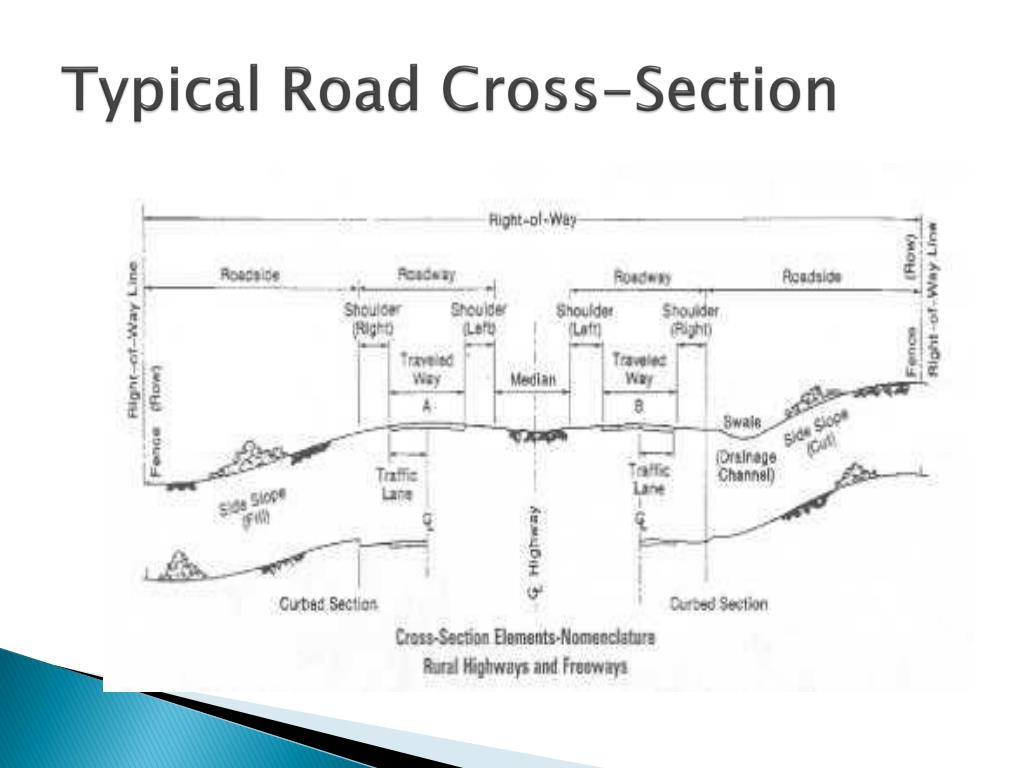
Right of way (ROW) Right of way (ROW) or land width is the width of land acquired for the road, along its alignment. It should be adequate to accommodate all the cross-sectional elements of the highway and may reasonably provide for future development. To prevent ribbon development along highways, control lines and building lines may be provided.
Typical Cross Section of Road 3D Warehouse
The term "cross section" is used to define the configuration of a proposed roadway at right an-gles to the centerline. Typical sections show the width, thickness and descriptions of the pavement section, as well as the geometrics of the graded roadbed, side ditches, and side slopes. Criteria are presented in two general catego-ries: (1.
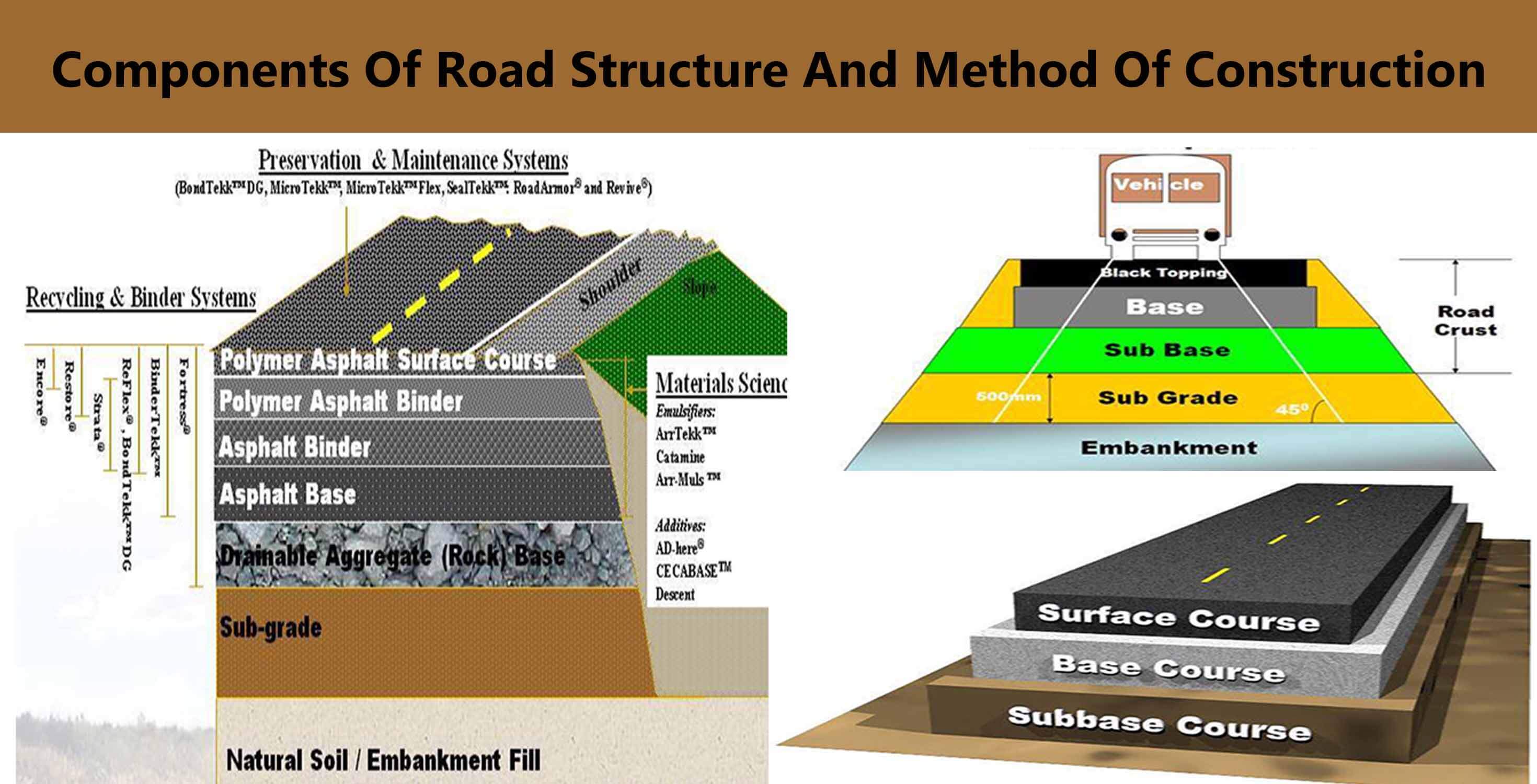
Components Of Road Structure And Method Of Construction Engineering Discoveries
9.3.15 - Railroad-Highway Grade Crossings. 9.3.16 - Pedestrian Considerations and Facilities. 9.3.17 - Bicycle Considerations and Facilities. 9.3.18 - Transit Considerations and Facilities. 9.3.19 - Parking Lot Layout Considerations. Section 9.4 - Resurfacing, Restoration and Rehabilitation (RRR) Design. 9.4.1 - Application of Design Standards.
OR 18 and OR 22 Road Improvement Design and Planning Project Preferred Concept
Design. The intersections of slope planes in the highway cross section should be well rounded for added safety, increased stability, and improved aesthetics. Front slopes, back slopes, and ditches should be sodded and/or seeded where feasible to promote stability and reduce erosion.

Cross Sectional Elements of Road, by Tutorials Tips Highway Engineering
Highway Cross-Section elements comprise the different features which form the effective width of the highway, These comprise the Right of way, Formation width, Shoulder, Berms, kerb, Carriageway, Building line, Control line, including other elements. All these elements have a vital role to play which makes each of these elements indispensable.

RoadCrossSectionInformationtoHelpYouUnderstandHowitWorks12 Engineering Feed
On divided highways, each one-way pavement has a unidirectional slope across the entire width of pavement. Except as allowed otherwise in 4.3.3. The tangent cross slope is 2 percent, withthe. The dimensions of a typical cross section depend upon a number of features that vary with the type of roadway. Geometric design standards as used by.
Basic Components of Road Structure and Method of Construction
follows, in 3.1.2, with a description of the two highway classification systems used in this chapter. Section 3.2 presents discussions of the individual elements as they relate to new construction. Section 3.3 focuses on some of these elements as they relate to resurfacing, restoration and rehabilitation work on existing facilities.
Typical Road Cross Section Drawing
1231.01 General. Geometric cross sections for state highways are governed by the need to balance performance metrics, the context, and selected design controls. The objective is to optimize the use of available public space while avoiding an unreasonable investment in right of way acquisition. The term "highways" refers to all WSDOT.

6 BASIC CROSS SECTIONAL ELEMENTS OF HIGHWAY PAVEMENT
Share. Revised: 9-Jan-2023FLH OpenRoads Designer User Manual Chapter 16This chapter covers the creation of Cross Sections and the procedure for the assembly Cross Section sheets for FLH Plan Set deliverables.

Image Figure 1 Typical cross section across road reserve.RCND14^2378801.JPG Road design
Road Structure Cross Section is composed of the following components: Surface/Wearing Course. Base Course. Sub Base. Sub Grade. 1. Surface/Wearing Course in pavement cross section: The top layers of pavement which is in direct contact with the wheel of the vehicle. Usually constructed of material in which bitumen is used as binder materials.
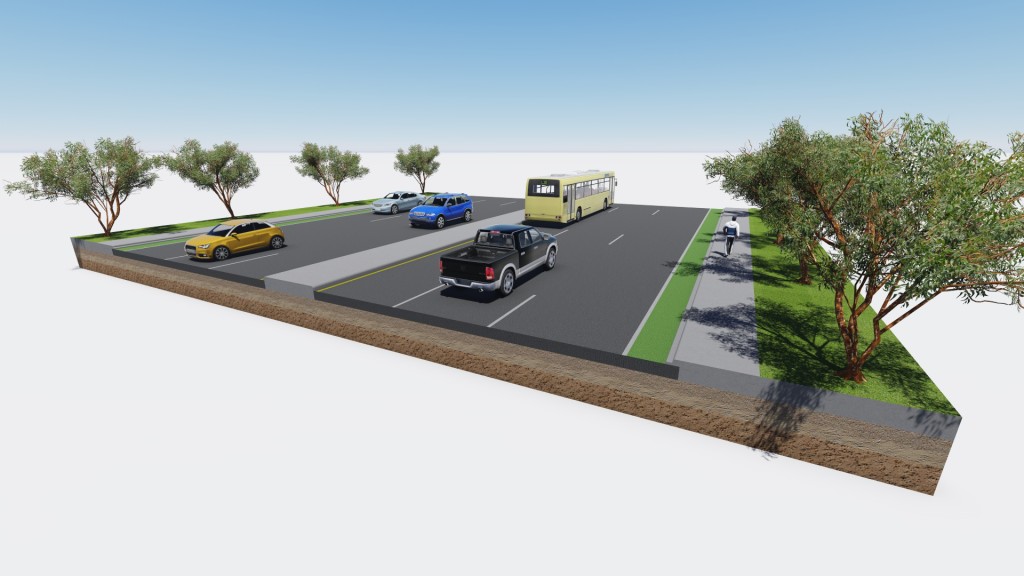

How to Make a 3D Road Cross Section Civil FX a division of Parametrix
Reading time: 3 minutes. The basic components of the highway are the road width, cross slope, pavement, road margins, traffic separators, and curbs. These geometric elements are designed and influenced by the psychology of the driver, the characteristics of the vehicle and the traffic of the region. Highway safety is ensured by fulfilling the.

Renewing the National Commitment to the Interstate Highway System A Foundation for the Future
Geometric design is the assembly of the fundamental three-dimensional features of the highway that are related to its operational quality and safety. Its basic objective is to provide a smooth-flowing, crash-free facility. Geometric roadway design consists of three main parts: cross section (lanes and shoulders, curbs, medians, roadside slopes.