
Sound infographic diagram including definition and example of playing piano releasing vibrations
A sound wave is a vibration that travels through a solid, liquid or gas such as the air or water. A loud sound has a large amplitude, a high pitched sound has a high frequency. Musicians and.

Loudness Easy Science Physics lessons, Science student, Science facts
A sound is a form of energy, just like electricity, heat or light. Sound is one of the important senses of the human body. Some sounds are pleasant, and some are annoying. We are subjected to various types of sound all time. Sound waves are the result of the vibration of objects. Let's examine some sources of sounds like a bell.

WhatisSound_1 Leverage Edu
Sound is a longitudinal, mechanical wave. Sound can travel through any medium, but it cannot travel through a vacuum. There is no sound in outer space. Sound is a variation in pressure. A region of increased pressure on a sound wave is called a compression (or condensation).
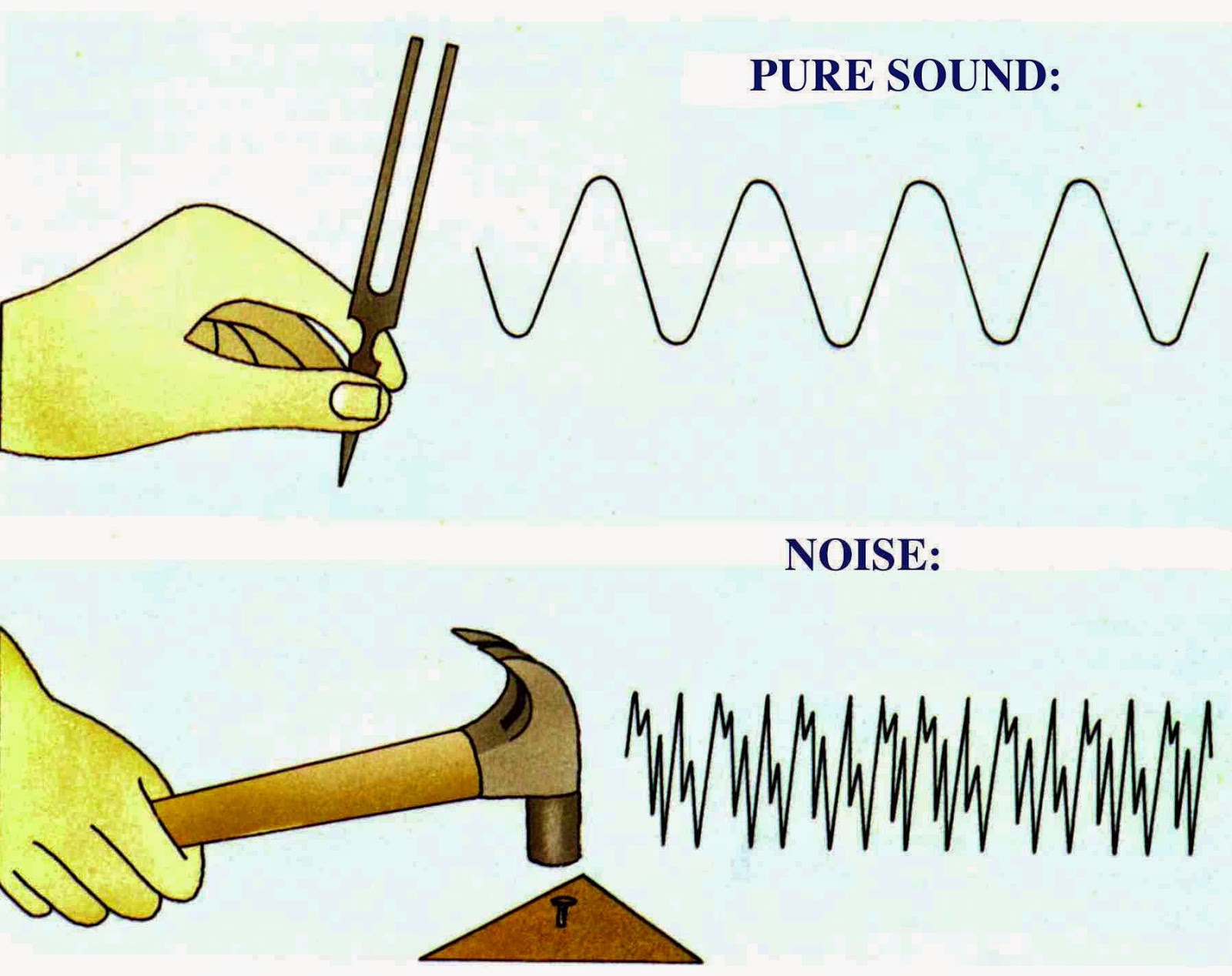
Science online How can the human ear differentiate between the sounds
Sound waves are longitudinal waves. They cause particles to vibrate parallel to the direction of wave travel. The. can travel through solids, liquids or gases. The speed of sound depends on the.
physics of sound
The period of a sound wave is the time it takes for an air molecule to oscillate back and forth one time. The wavelength of a sound wave is the distance between two compressed regions of air. People get these mixed up because there's an alternate way to create a graph of this sound wave. Consider this.

Echoes and Vibrations of Sound ICSE Solutions for Class 10 Physics A Plus Topper
Sound. Sound is a vibration or disturbance that travel through any medium by transferring energy from one particle to other and can be heard when it reaches a person's or animal's ear. For example when an object vibrates it transfers its energy to the surrounding particles and makes them to vibrate.These particles again collide with the other.

Wavelength of Sound Waves Class 9 Science Notes by Teachoo
17.2: Sound Waves. Sound is a disturbance of matter (a pressure wave) that is transmitted from its source outward. Hearing is the perception of sound. Sound can be modeled in terms of pressure or in terms of displacement of molecules. The human ear is sensitive to frequencies between 20 Hz and 20 kHz.

Physics Intro or Basics of Sound Waves YouTube
On the atomic scale, sound is a disturbance of atoms that is far more ordered than their thermal motions. In many instances, sound is a periodic wave, and the atoms undergo simple harmonic motion. Thus, sound waves can induce oscillations and resonance effects ( Figure 17.2 ).
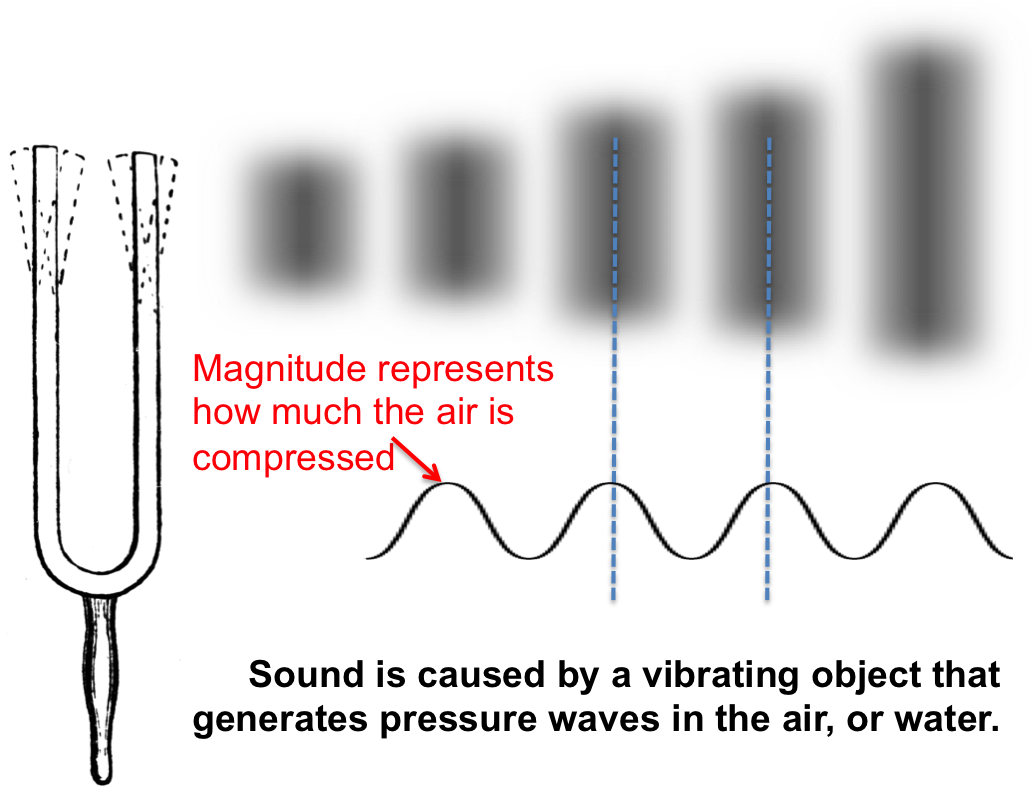
PhysicsWhat is sound?
17.3: Sound Intensity. Intensity I = P A P A is the same for a sound wave as was defined for all waves, where P is the power crossing area A. The SI unit for I is watts per meter squared. The intensity of a sound wave is also related to the pressure amplitude Δ Δ p: I = (Δp)2 2ρv (17.S.22) (17.S.22) I = ( Δ p) 2 2 ρ v.

Loudness, Intensity, Pitch and Quality of Sound Teachoo
In physics, sound is a vibration that propagates as an acoustic wave through a transmission medium such as a gas, liquid or solid. In human physiology and psychology, sound is the reception of such waves and their perception by the brain. [1]
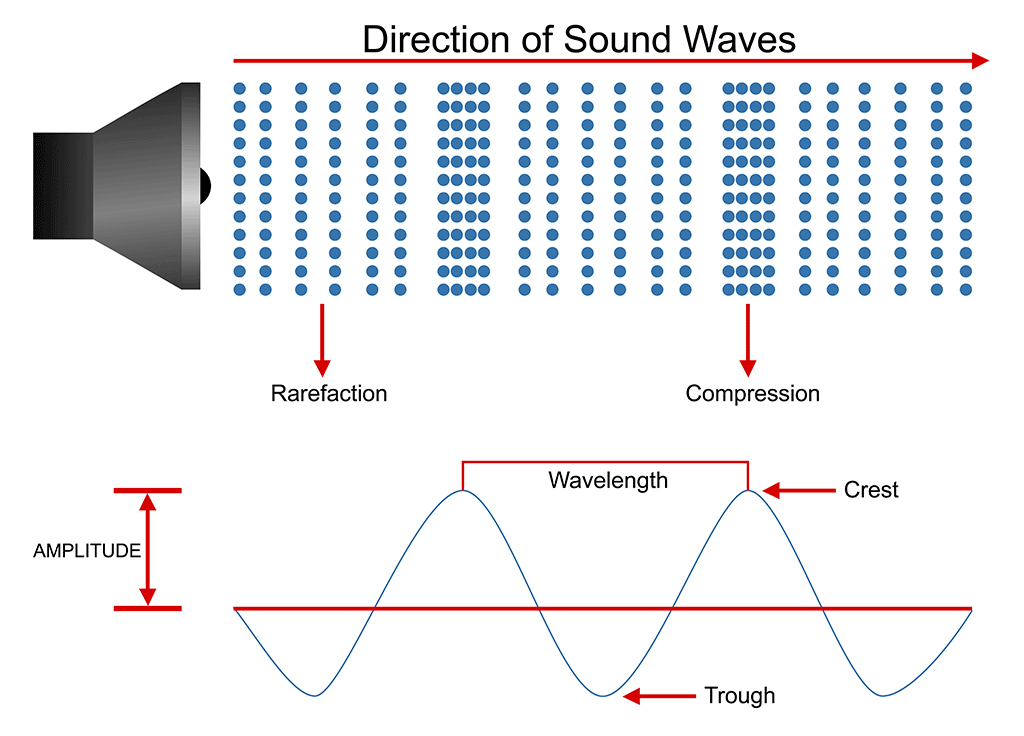
Sound Waves PASCO
Sound will also travel through a solid, but in that case the interactions of the particles are different than in a fluid, and the constant that takes the place of tension is a different one: Young's modulus. But the formula looks the same: vsound in solid = Y ρ−−√ (2.1.2) (2.1.2) v s o u n d i n s o l i d = Y ρ.
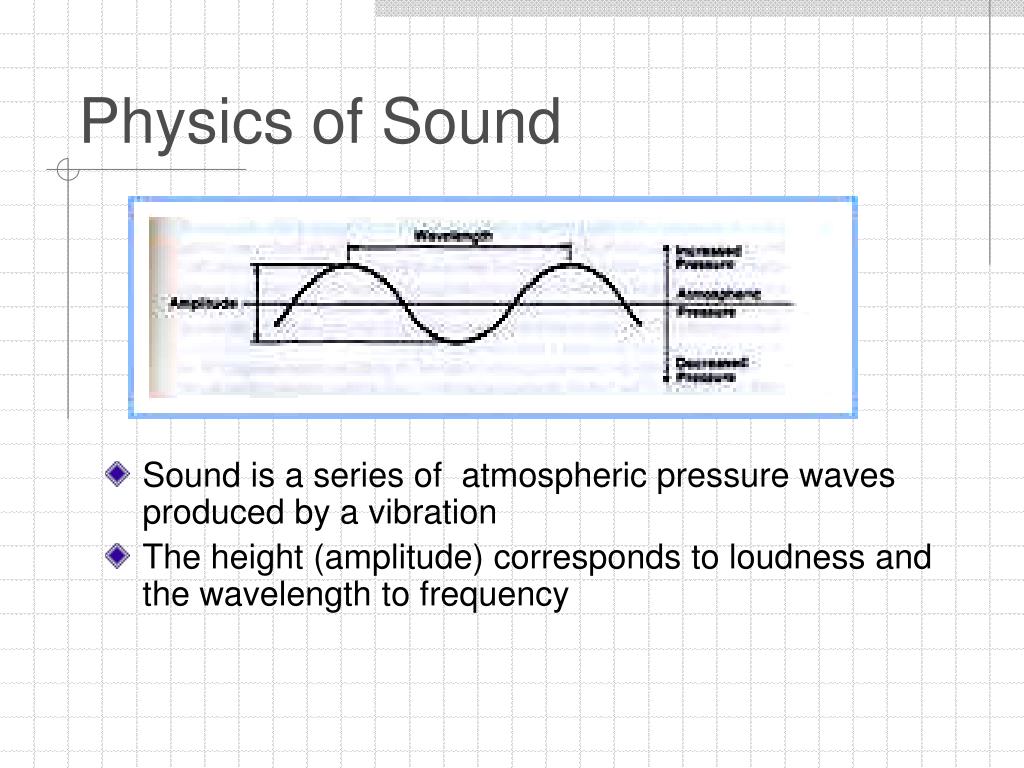
PPT Physics of Sound PowerPoint Presentation, free download ID70345
Home Bookshelves University Physics University Physics (OpenStax) University Physics I - Mechanics, Sound, Oscillations, and Waves (OpenStax)
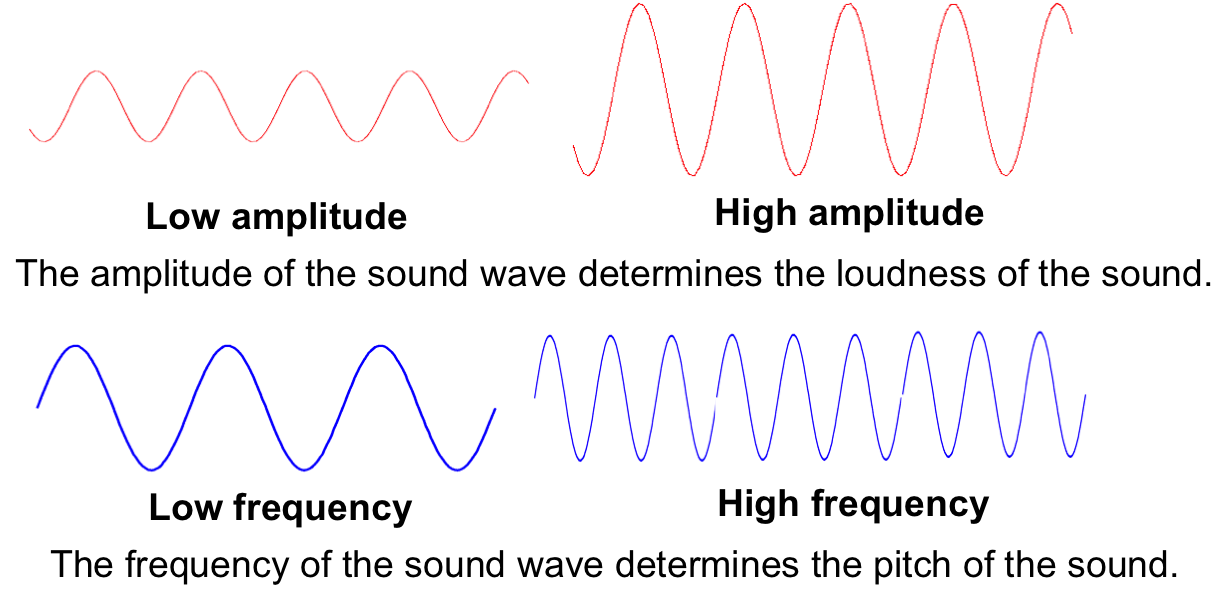
PhysicsWhat is sound?
The speed or velocity at which sound travels through a medium is dependent upon the density and the elasticity of the medium. The three important terms that are the basics for understanding the physics of sound are sound pressure, sound power, and sound intensity. Sound pressure is defined as the difference between atmospheric pressure and the.
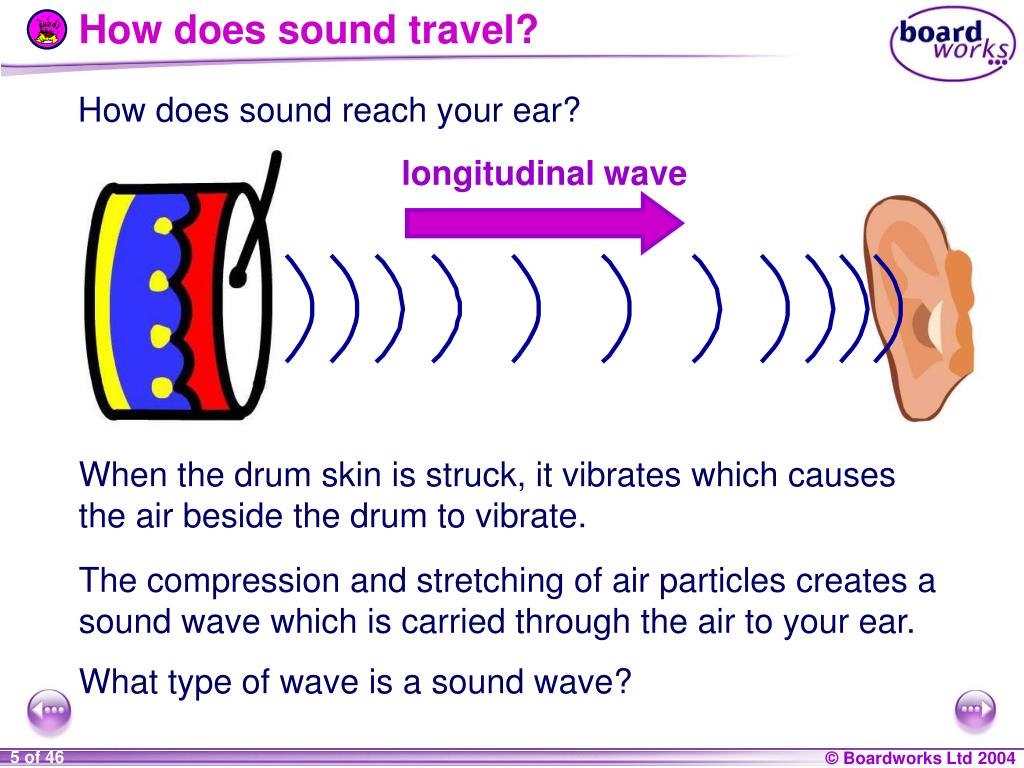
PPT KS4 Physics PowerPoint Presentation, free download ID6014491
Sound is a Pressure Wave Lesson 2 - Sound Properties and Their Perception Pitch and Frequency Intensity and the Decibel Scale The Speed of Sound The Human Ear Lesson 3 Behavior of Sound Waves Interference and Beats The Doppler Effect and Shock Waves Boundary Behavior Reflection, Refraction, and Diffraction Lesson 4 - Resonance and Standing Waves

PPT Physics of Sound PowerPoint Presentation, free download ID70345
sound, Mechanical disturbance that propagates as a longitudinal wave through a solid, liquid, or gas. A sound wave is generated by a vibrating object. The vibrations cause alternating compressions (regions of crowding) and rarefactions (regions of scarcity) in the particles of the medium. The particles move back and forth in the direction of.

PPT PHYSICS OF SOUND PowerPoint Presentation, free download ID5938395
Sound is a wave. On the atomic scale, it is a disturbance of atoms that is far more ordered than their thermal motions. In many instances, sound is a periodic wave, and the atoms undergo simple harmonic motion. In this text, we shall explore such periodic sound waves.