PPT Chapter 6 Enzymes PowerPoint Presentation ID5143485
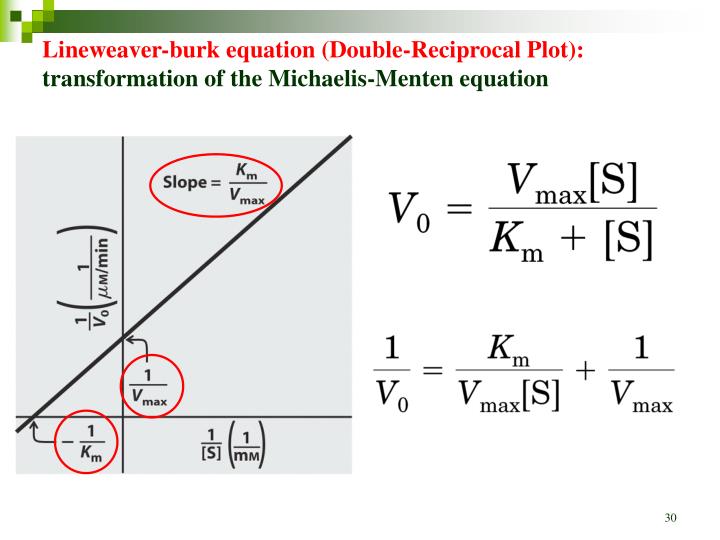
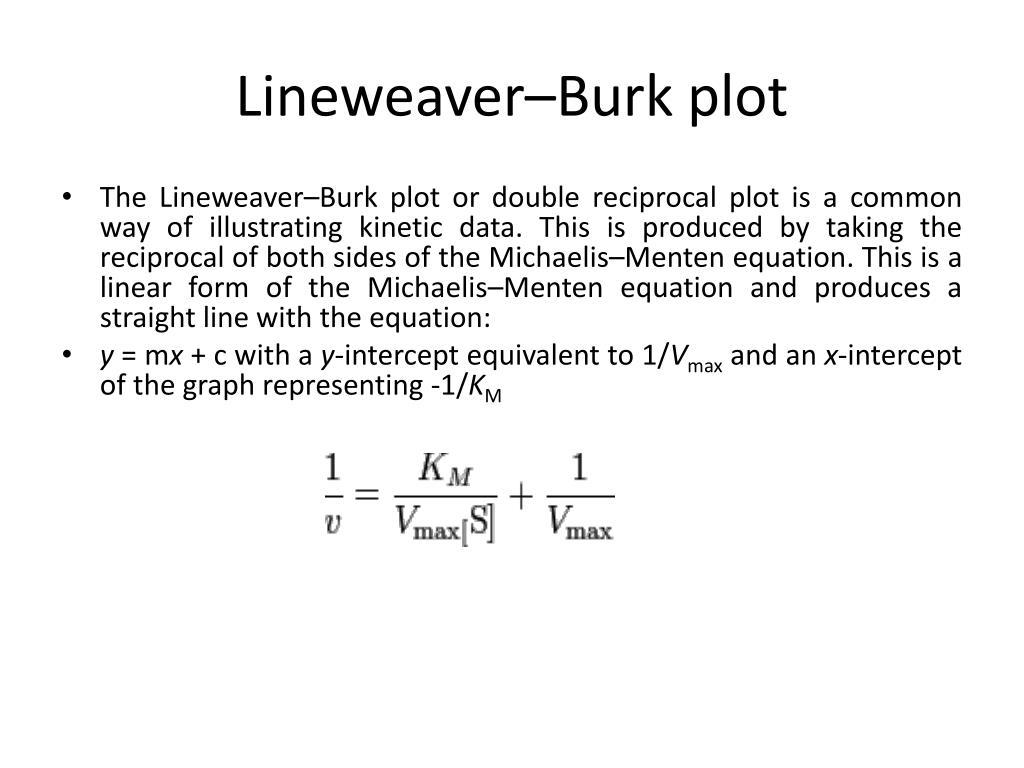
Lineweaver-Burke (the "double reciprocal" plot) The Michaelis-Menten equation can be rearranged by taking the reciprocal, to yield: If X = 1/[S] and Y=1/V then this is a linear equation with a slope of K m /V max and a Y intercept of 1/V max; Figure 6.2.3: 1/S and1/V.

LineweaverBurk plots of reaction velocity versus substrate... Download Scientific Diagram
affect the plots. A comparison between the two graphic representations direct is illustrated here with two "bad" data points (see Fig. 8.16, WWBH). •The same data points are plotted on adjacent Lineweaver-Burk in the left graph of this figure. Two features of the direct linear plot are immediately evident by comparison.
PPT Chemistry 232 PowerPoint Presentation, free download ID382916
In biochemistry, the Lineweaver Burk Equation of energy kinetics results in a Lineweaver Burk Plot also known as a Double Reciprocal Plot. Therefore, users may wonder how to make a Lineweaver Burk plot in Excel. In this article, we demonstrate step-by-step procedures to make a Lineweaver Burk plot in Excel. Table of Contents Expand

LineweaverBurk plot to determine the Monod constants for... Download Scientific
Another commonly-used plot in examining enzyme kinetics is the Lineweaver-Burk plot, in with the inverse of the reaction rate, \(1/r\), is plotted against the inverse of the substrate concentration \(1/\left[ \text{S} \right]\). Rearranging Equation \(\ref{Eq13.26}\),. Figure 13.12: Linweaver-Burk plot and regression equation for the data.
Lineweaver Burk plot. The data on Xaxis indicate the 1/substrate while... Download Scientific
Tthe Lineweaver-Burk plot (or double reciprocal plot) is a graphical representation of the Lineweaver-Burk equation of enzyme kinetics, described by Hans Lineweaver and Dean Burk in 1934 (Figure \(\PageIndex{2}\)).. Lineweaver-Burk plot of Michaelis-Menten kineitcs. The plot provides a useful graphical method for analysis of the.
Solved Using the LineweaverBurk plot below, what is the Km
The Lineweaver-Burk plot (or double reciprocal plot) is a graphical representation of the Lineweaver-Burk equation of enzyme kinetics, described by Hans Lineweaver and Dean Burk in 1934. This plot is a derivation of the Michaelis-Menten equation and is represented as: Table of Contents
13.2 Chemical Chemistry LibreTexts
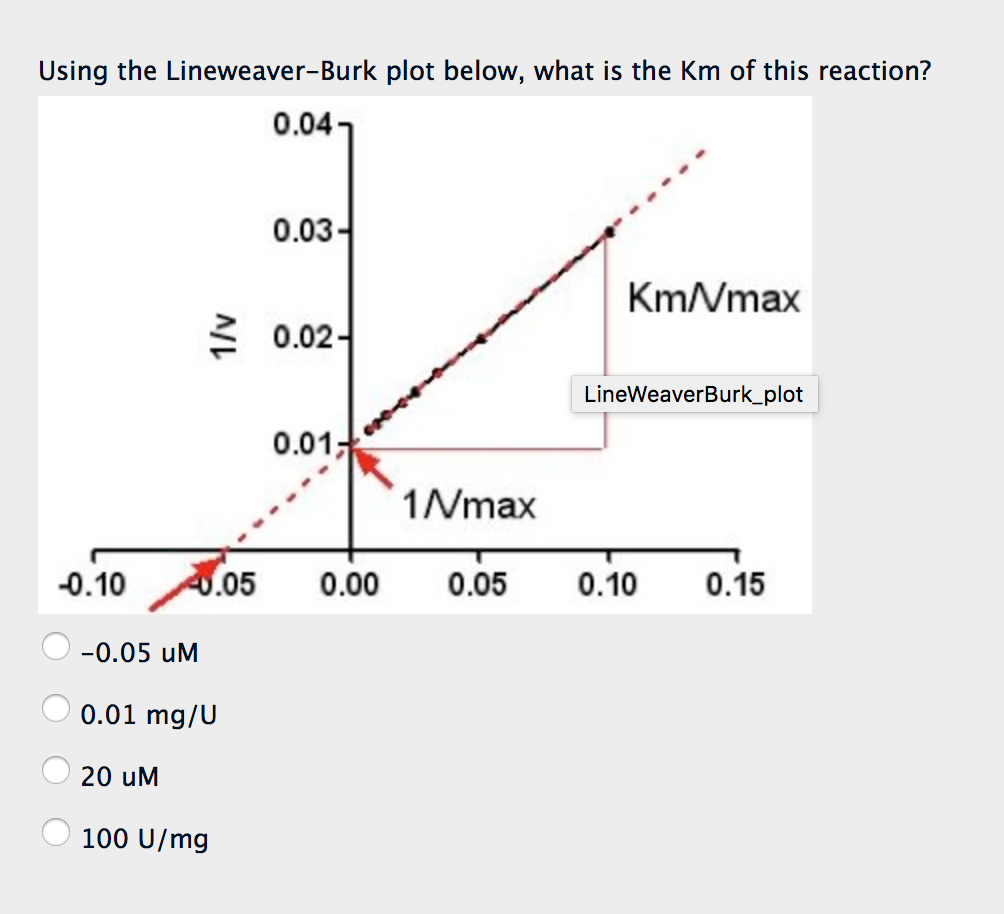
5 4 Problem To determine the V max from a Lineweaver-Burk plot you would: A Multiply the reciprocal of the x-axis intercept by -1. B Multiply the reciprocal of the y-axis intercept by -1. C Take the reciprocal of the x-axis intercept. D

SOLUTION Lineweaver burk eadie hofstee hanes plot derivation from michaelis menten equation
Lineweaver-Burk plot with data points derived from double-reciprocal transformation, but we'll superimpose a line based upon nonlinear regression analysis, so that it reflects the best possible estimates of K m and V max. A different secondary plot, such as Hanes-Woolf or Eadie-Scatchard, is just as easy to create with Prism.

(A) LineweaverBurk plot for the inhibition of eeAChE(A) and eqBChE (B)... Download Scientific
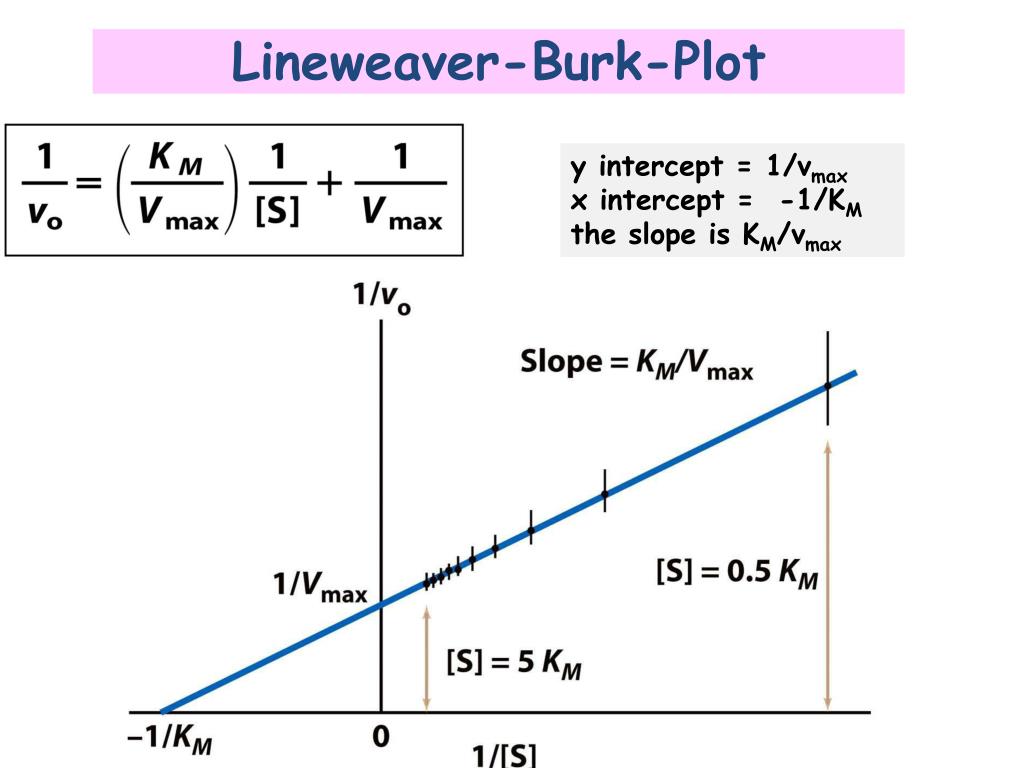
Lineweaver-Burk Plots. The Michaelis-Menten equation is useful in other ways, too. If we take its inverse, we get a new relationship. That's useful because it's really an expression for a straight line. If we plot 1/v against 1/[S], we get a straight line. The slope is K m /V max and the y intercept is 1/V max. Lineweaver-Burk plot gives a.
PPT Lecture 4 PowerPoint Presentation, free download ID2832807
The Lineweaver-Burk equation calculator computes the inverse of the initial velocity of an enzyme inhibited reaction INSTRUCTIONS: Enter the following: (Vmax) Maximum Velocity of Reaction in moles/(Liter⋅Seconds) [S] Concentration of Substrate [Km] Michaelis-Menten Constant Inverse Velocity (1/V0): The calculator returns the inverse velocity in seconds-liters per mole (s·L/mol) The Math.

LineweaverBurk Equation Theory and Derivation YouTube
double reciprocal plot (e.g., Lineweaver-Burk plot discussed below;. Figure 13.12: Linweaver-Burk plot and regression equation for the data in Example 13.6.-diphenyl oxidase. The following data are for the oxidation of catechol (the substrate) to o-quinone by the enzyme o-diphenyl oxidase. The reaction is followed by monitoring the.

reaction mechanism Enzyme Given Km find substrate concentration at a certain
The Lineweaver-Burk equation of enzyme kinetics is represented graphically by the Lineweaver-Burk Plot (also known as the double reciprocal plot), which was first introduced by Dean Burk and Hans Lineweaver in 1934. It is difficult to predict Vmax and, consequently, Km from a hyperbolic plot since Vmax is reached at an infinite substrate.

How to Calculate Km Sciencing
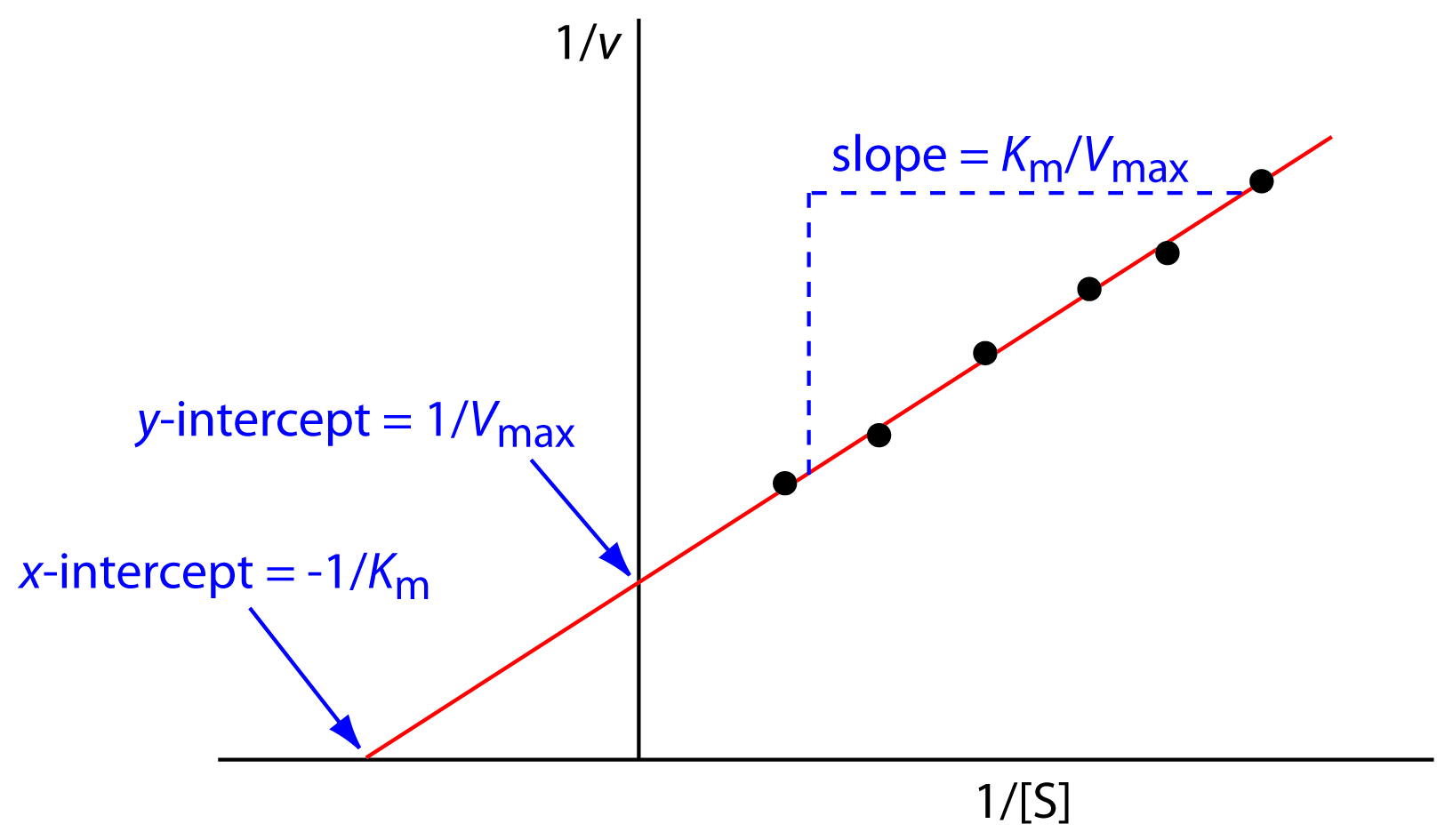
Figure 4.9.1: Line-Weaver Burk Plot. For a Lineweaver-Burk, the manipulation is using the reciprocal of the values of both the velocity and the substrate concentration. The inverted values are then plotted on a graph as 1 / V vs. 1 / [ S ]. Because of these inversions, Lineweaver-Burk plots are commonly referred to as 'double-reciprocal' plots.

LineweaverBurk plot of the inhibition of nitric oxide synthase... Download Scientific Diagram
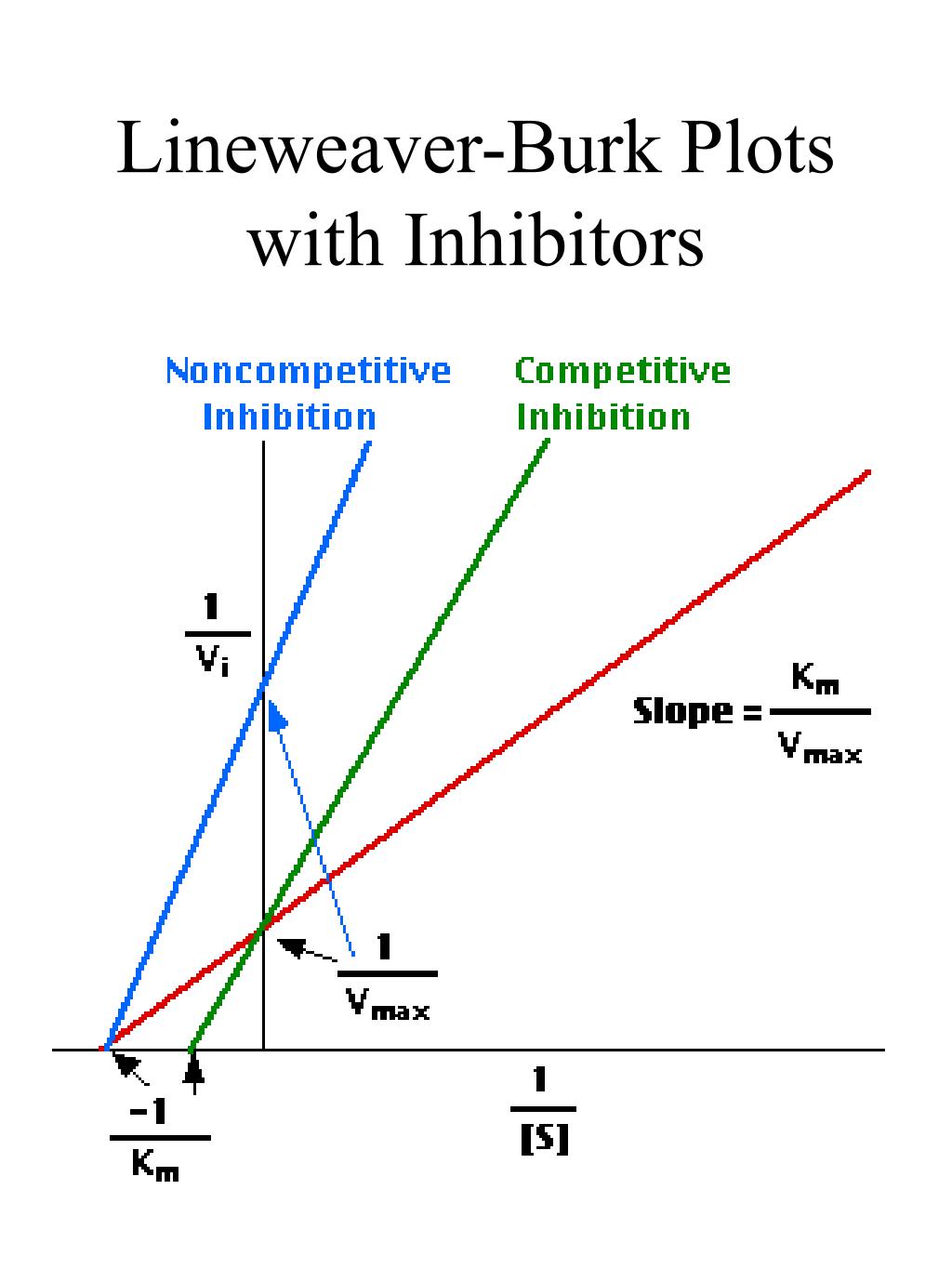
The double reciprocal plot (Lineweaver Burk plot) offers a great way to visualize the inhibition. In the presence of I, just Vm will decrease. Therefore, -1/Km, the x-intercept will stay the same, and \(1/V_m\) will get more positive.. An equation, shown in the diagram above can be derived which shows the effect of the noncompetitive.
PPT 513341 Biochemistry I Chapter 7 ENZYME PowerPoint Presentation ID4312460
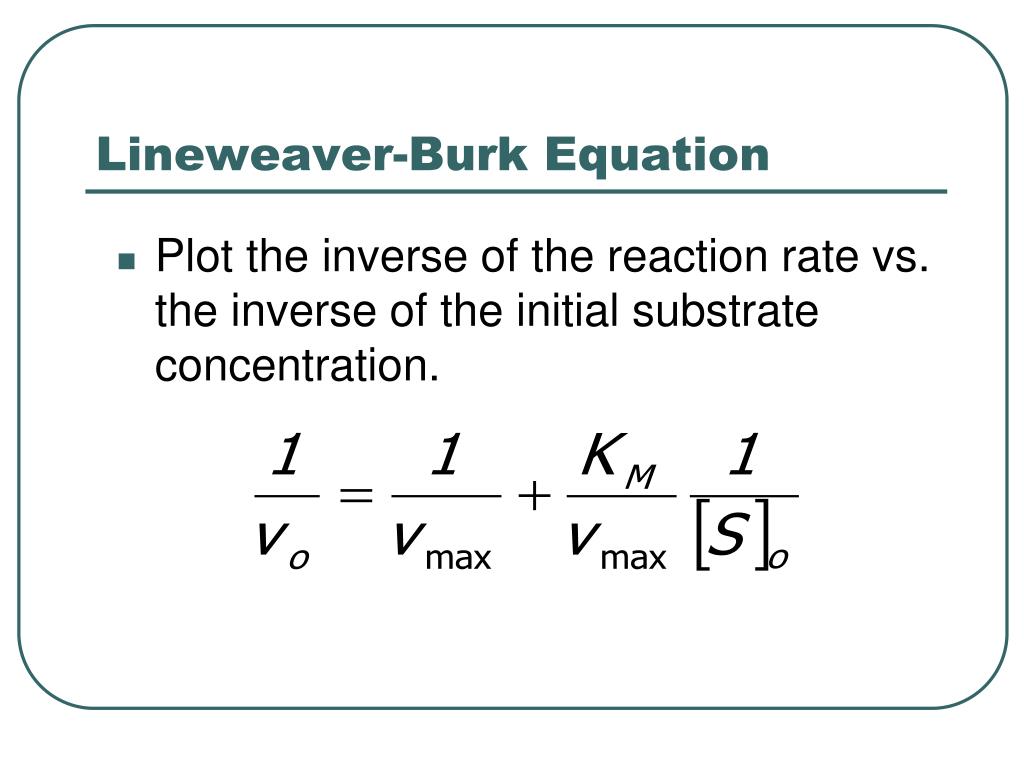
Lineweaver-Burk analysis is one method of linearizing substrate-velocity data so as to determine the kinetic constants Km and Vmax. One creates a secondary, reciprocal plot: 1/velocity vs. 1/ [substrate].
PPT LAB 3 Enzyme PowerPoint Presentation, free download ID4526880
Lineweaver-Burke (the "double reciprocal" plot) The Michaelis-Menten equation can be rearranged by taking the reciprocal, to yield: If X = 1/[S] and Y=1/V then this is a linear equation with a slope of K m /V max and a Y intercept of 1/V max; Figure 6.2.3: 1/S and1/V